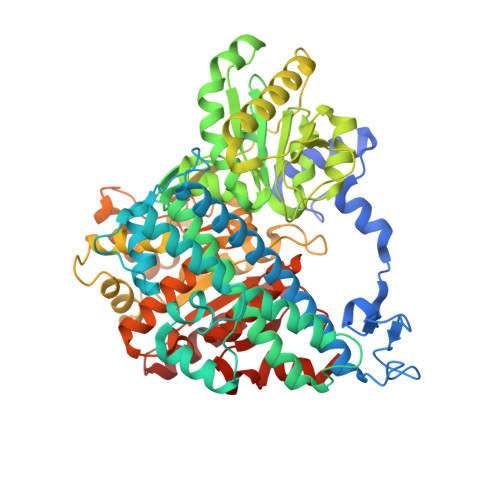
Identifying a key spot for electron mediator-interaction to tailor CO dehydrogenase's affinity.
Kim, S.M., Kang, S.H., Lee, J., Heo, Y., Poloniataki, E.G., Kang, J., Yoon, H.J., Kong, S.Y., Yun, Y., Kim, H., Ryu, J., Lee, H.H., Kim, Y.H.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 2732-2732
- PubMed: 38548760
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46909-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8X9D, 8X9E, 8X9F, 8X9G, 8X9H - PubMed Abstract:
Fe‒S cluster-harboring enzymes, such as carbon monoxide dehydrogenases (CODH), employ sophisticated artificial electron mediators like viologens to serve as potent biocatalysts capable of cleaning-up industrial off-gases at stunning reaction rates. Unraveling the interplay between these enzymes and their associated mediators is essential for improving the efficiency of CODHs. Here we show the electron mediator-interaction site on ChCODHs (Ch, Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans) using a systematic approach that leverages the viologen-reactive characteristics of superficial aromatic residues. By enhancing mediator-interaction (R57G/N59L) near the D-cluster, the strategically tailored variants exhibit a ten-fold increase in ethyl viologen affinity relative to the wild-type without sacrificing the turn-over rate (k cat ). Viologen-complexed structures reveal the pivotal positions of surface phenylalanine residues, serving as external conduits for the D-cluster to/from viologen. One variant (R57G/N59L/A559W) can treat a broad spectrum of waste gases (from steel-process and plastic-gasification) containing O 2 . Decoding mediator interactions will facilitate the development of industrially high-efficient biocatalysts encompassing gas-utilizing enzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), 50 UNIST-gil, Ulsan, 44919, Republic of Korea. smkimlife@unist.ac.kr.