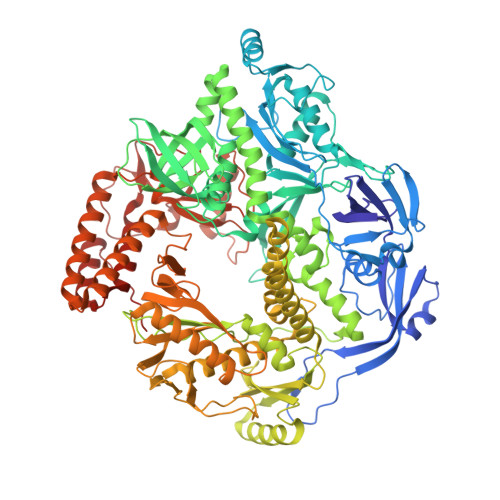
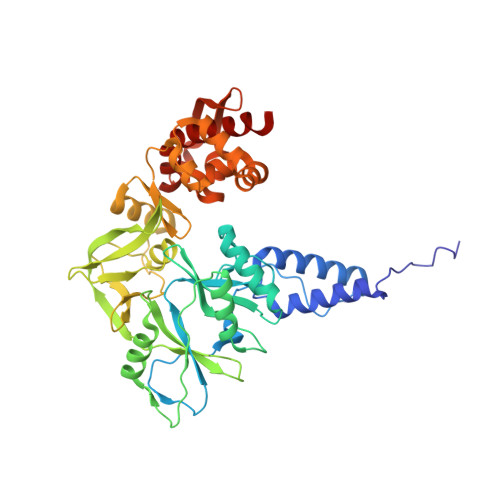
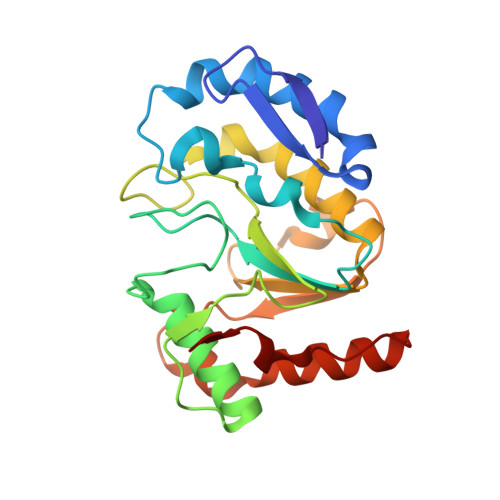
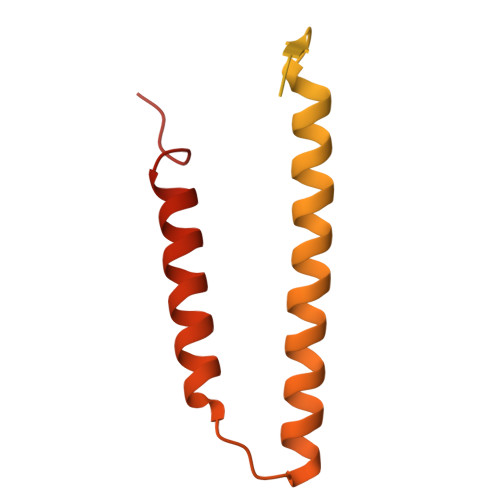
Structural insights into the assembly and mechanism of mpox virus DNA polymerase complex F8-A22-E4-H5.
Wang, X., Ma, L., Li, N., Gao, N.(2023) Mol Cell 83: 4398
- PubMed: 37995690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.10.038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WPE, 8WPF, 8WPK, 8WPP - PubMed Abstract:
The DNA replication of mpox virus is performed by the viral polymerase F8 and also requires other viral factors, including processivity factor A22, uracil DNA glycosylase E4, and phosphoprotein H5. However, the molecular roles of these viral factors remain unclear. Here, we characterize the structures of F8-A22-E4 and F8-A22-E4-H5 complexes in the presence of different primer-template DNA substrates. E4 is located upstream of F8 on the template single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and is catalytically active, highlighting a functional coupling between DNA base-excision repair and DNA synthesis. Moreover, H5, in the form of tetramer, binds to the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) region downstream of F8 in a similar position as PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) does in eukaryotic polymerase complexes. Omission of H5 or disruption of its DNA interaction showed a reduced synthesis of full-length DNA products. These structures provide snapshots for the working cycle of the polymerase and generate insights into the mechanisms of these essential factors in viral DNA replication.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Peking-Tsinghua Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.