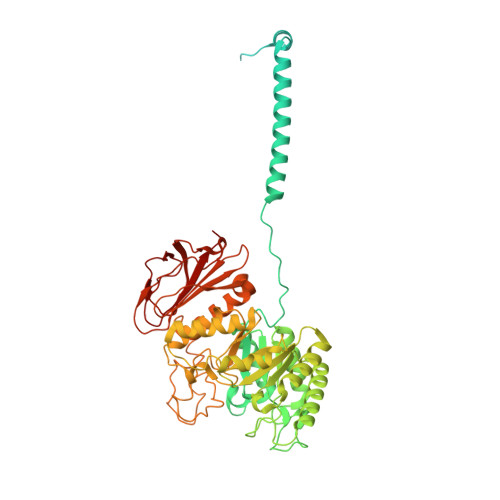
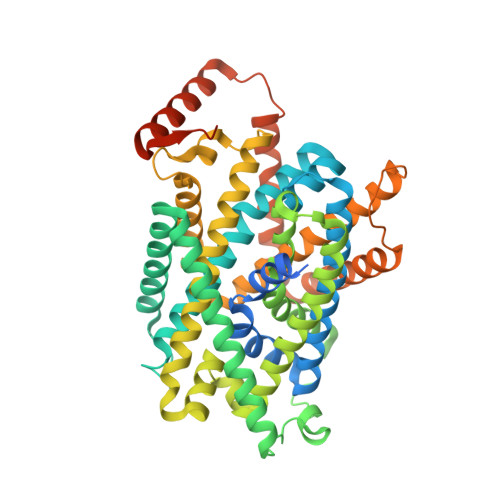
Cryo-EM structure of the human Asc-1 transporter complex.
Li, Y., Guo, Y., Broer, A., Dai, L., Brӧer, S., Yan, R.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 3036-3036
- PubMed: 38589439
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47468-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WNS, 8WNT, 8WNY - PubMed Abstract:
The Alanine-Serine-Cysteine transporter 1 (Asc-1 or SLC7A10) forms a crucial heterodimeric transporter complex with 4F2hc (SLC3A2) through a covalent disulfide bridge. This complex enables the sodium-independent transport of small neutral amino acids, including L-Alanine (L-Ala), Glycine (Gly), and D-Serine (D-Ser), within the central nervous system (CNS). D-Ser and Gly are two key endogenous glutamate co-agonists that activate N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors by binding to the allosteric site. Mice deficient in Asc-1 display severe symptoms such as tremors, ataxia, and seizures, leading to early postnatal death. Despite its physiological importance, the functional mechanism of the Asc-1-4F2hc complex has remained elusive. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the human Asc-1-4F2hc complex in its apo state, D-Ser bound state, and L-Ala bound state, resolved at 3.6 Å, 3.5 Å, and 3.4 Å, respectively. Through detailed structural analysis and transport assays, we uncover a comprehensive alternating access mechanism that underlies conformational changes in the complex. In summary, our findings reveal the architecture of the Asc-1 and 4F2hc complex and provide valuable insights into substrate recognition and the functional cycle of this essential transporter complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Key University Laboratory of Metabolism and Health of Guangdong, School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China.