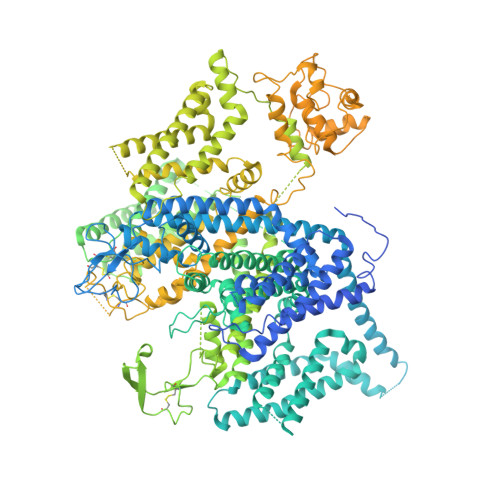
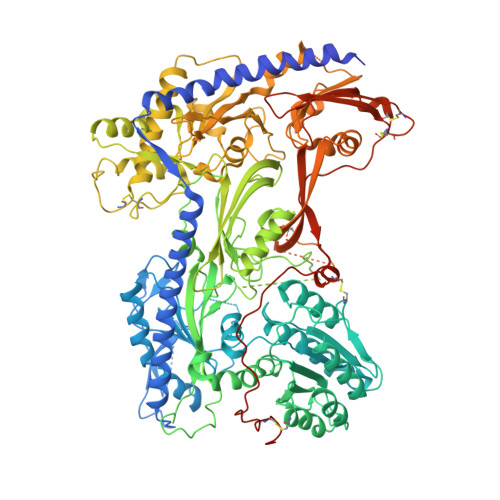
Structural basis for human Ca v 1.2 inhibition by multiple drugs and the neurotoxin calciseptine.
Gao, S., Yao, X., Chen, J., Huang, G., Fan, X., Xue, L., Li, Z., Wu, T., Zheng, Y., Huang, J., Jin, X., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Yu, Y., Liu, L., Pan, X., Song, C., Yan, N.(2023) Cell 186: 5363-5374.e16
- PubMed: 37972591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.10.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FHS, 8WE6, 8WE7, 8WE8, 8WE9, 8WEA - PubMed Abstract:
Ca v 1.2 channels play crucial roles in various neuronal and physiological processes. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human Ca v 1.2, both in its apo form and in complex with several drugs, as well as the peptide neurotoxin calciseptine. Most structures, apo or bound to calciseptine, amlodipine, or a combination of amiodarone and sofosbuvir, exhibit a consistent inactivated conformation with a sealed gate, three up voltage-sensing domains (VSDs), and a down VSD II . Calciseptine sits on the shoulder of the pore domain, away from the permeation path. In contrast, when pinaverium bromide, an antispasmodic drug, is inserted into a cavity reminiscent of the IFM-binding site in Na v channels, a series of structural changes occur, including upward movement of VSD II coupled with dilation of the selectivity filter and its surrounding segments in repeat III. Meanwhile, S4-5 III merges with S5 III to become a single helix, resulting in a widened but still non-conductive intracellular gate.
- Department of Urology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China; Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA. Electronic address: gaoshuai812@whu.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: