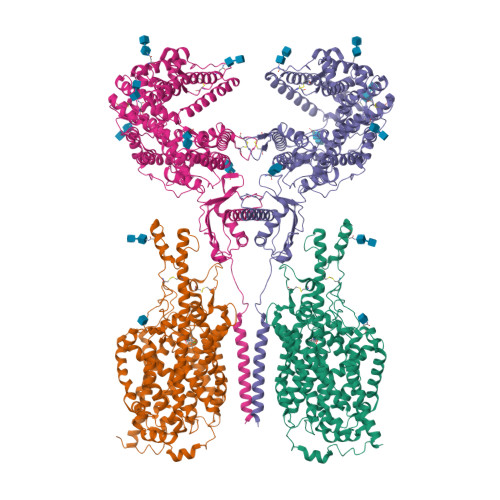
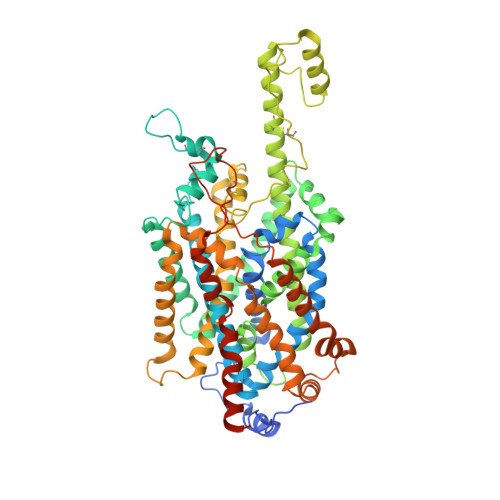
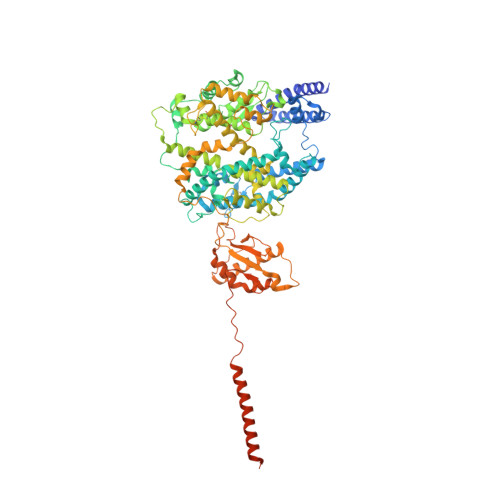
Molecular basis of inhibition of the amino acid transporter B 0 AT1 (SLC6A19).
Xu, J., Hu, Z., Dai, L., Yadav, A., Jiang, Y., Broer, A., Gardiner, M.G., McLeod, M., Yan, R., Broer, S.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 7224-7224
- PubMed: 39174516
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51748-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WBY, 8WBZ - PubMed Abstract:
The epithelial neutral amino acid transporter B 0 AT1 (SLC6A19) is the major transporter for the absorption of neutral amino acids in the intestine and their reabsorption in the kidney. Mouse models have demonstrated that lack of B 0 AT1 can normalize elevated plasma amino acids in rare disorders of amino acid metabolism such as phenylketonuria and urea-cycle disorders, implying a pharmacological approach for their treatment. Here we employ a medicinal chemistry approach to generate B 0 AT1 inhibitors with IC 50 -values of 31-90 nM. High-resolution cryo-EM structures of B 0 AT1 in the presence of two compounds from this series identified an allosteric binding site in the vestibule of the transporter. Mechanistically, binding of these inhibitors prevents a movement of TM1 and TM6 that is required for the transporter to make a conformational change from an outward open state to the occluded state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, Australia.