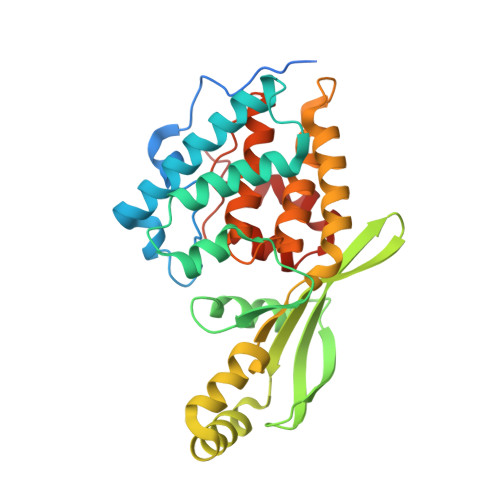
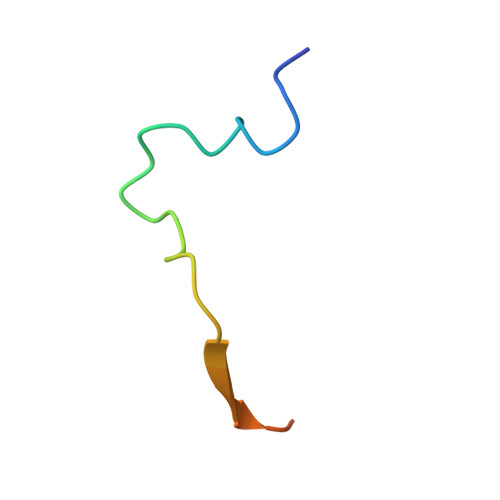
Pseudomonas effector AvrB is a glycosyltransferase that rhamnosylates plant guardee protein RIN4.
Peng, W., Garcia, N., Servage, K.A., Kohler, J.J., Ready, J.M., Tomchick, D.R., Fernandez, J., Orth, K.(2024) Sci Adv 10: eadd5108-eadd5108
- PubMed: 38354245
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.add5108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TWJ, 8TWO, 8TWS, 8TXF - PubMed Abstract:
The plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae encodes a type III secretion system avirulence effector protein, AvrB, that induces a form of programmed cell death called the hypersensitive response in plants as a defense mechanism against systemic infection. Despite the well-documented catalytic activities observed in other Fido ( Fi c, Do c, and AvrB) proteins, the enzymatic activity and target substrates of AvrB have remained elusive. Here, we show that AvrB is an unprecedented glycosyltransferase that transfers rhamnose from UDP-rhamnose to a threonine residue of the Arabidopsis guardee protein RIN4. We report structures of various enzymatic states of the AvrB-catalyzed rhamnosylation reaction of RIN4, which reveal the structural and mechanistic basis for rhamnosylation by a Fido protein. Collectively, our results uncover an unexpected reaction performed by a prototypical member of the Fido superfamily while providing important insights into the plant hypersensitive response pathway and foreshadowing more diverse chemistry used by Fido proteins and their substrates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.