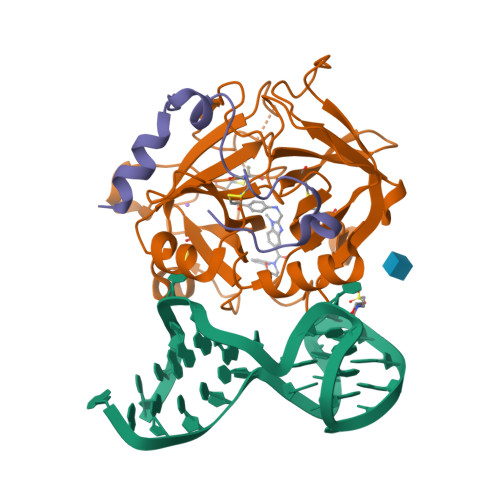
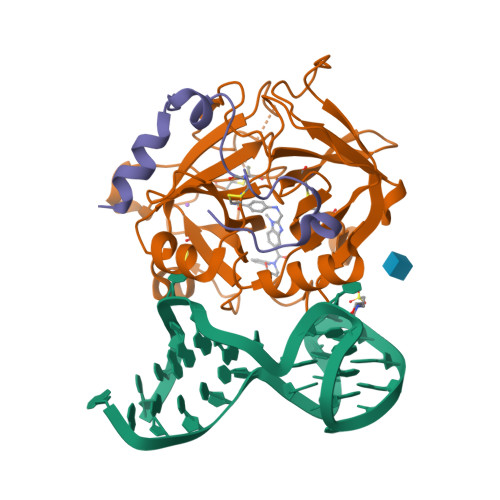
Aptameric hirudins as selective and reversible EXosite-ACTive site (EXACT) inhibitors.
Yu, H., Kumar, S., Frederiksen, J.W., Kolyadko, V.N., Pitoc, G., Layzer, J., Yan, A., Rempel, R., Francis, S., Krishnaswamy, S., Sullenger, B.A.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 3977-3977
- PubMed: 38730234
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48211-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TQS - PubMed Abstract:
Potent and selective inhibition of the structurally homologous proteases of coagulation poses challenges for drug development. Hematophagous organisms frequently accomplish this by fashioning peptide inhibitors combining exosite and active site binding motifs. Inspired by this biological strategy, we create several EXACT inhibitors targeting thrombin and factor Xa de novo by linking EXosite-binding aptamers with small molecule ACTive site inhibitors. The aptamer component within the EXACT inhibitor (1) synergizes with and enhances the potency of small-molecule active site inhibitors by many hundred-fold (2) can redirect an active site inhibitor's selectivity towards a different protease, and (3) enable efficient reversal of inhibition by an antidote that disrupts bivalent binding. One EXACT inhibitor, HD22-7A-DAB, demonstrates extraordinary anticoagulation activity, exhibiting great potential as a potent, rapid onset anticoagulant to support cardiovascular surgeries. Using this generalizable molecular engineering strategy, selective, potent, and rapidly reversible EXACT inhibitors can be created against many enzymes through simple oligonucleotide conjugation for numerous research and therapeutic applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Surgery, Duke University, Durham, NC, USA.