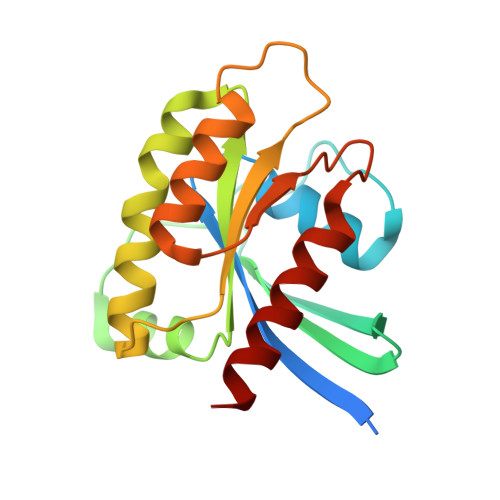
Strain-release alkylation of Asp12 enables mutant selective targeting of K-Ras-G12D.
Zheng, Q., Zhang, Z., Guiley, K.Z., Shokat, K.M.(2024) Nat Chem Biol 20: 1114-1122
- PubMed: 38443470
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-024-01565-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
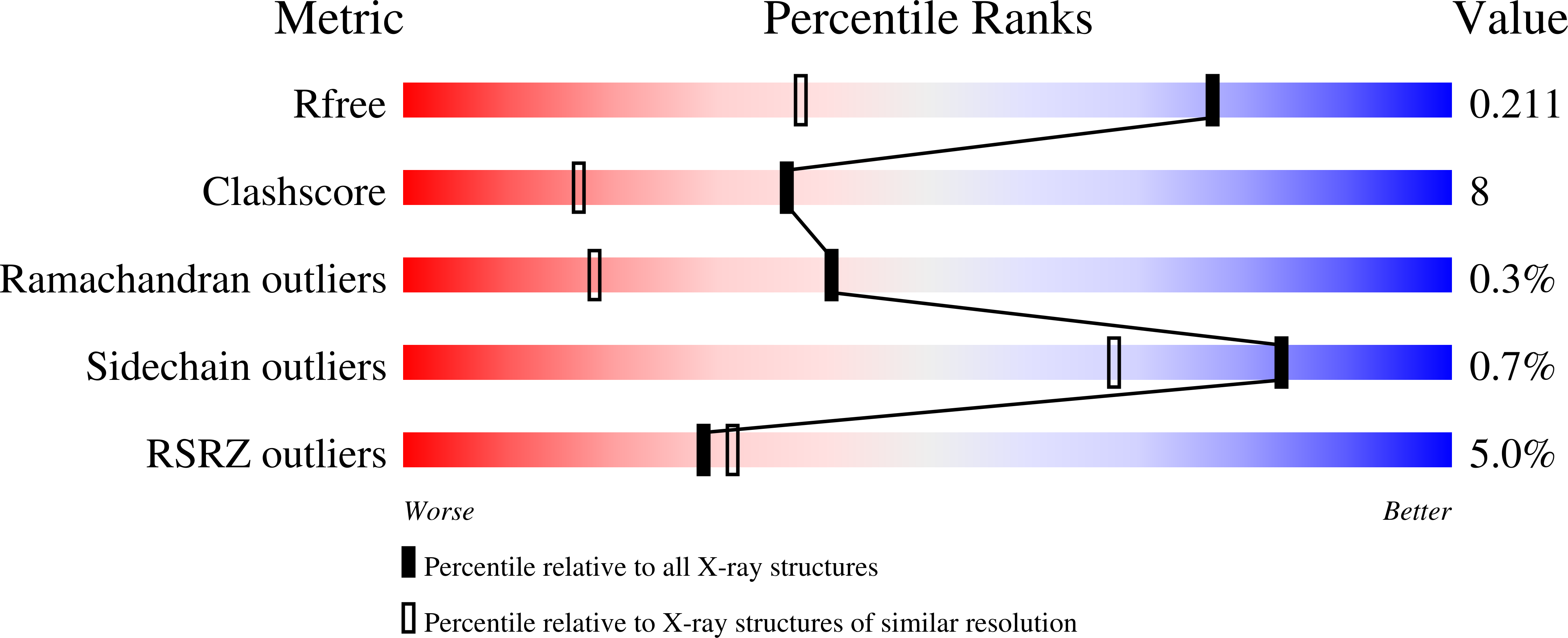
8T4V - PubMed Abstract:
K-Ras is the most commonly mutated oncogene in human cancer. The recently approved non-small cell lung cancer drugs sotorasib and adagrasib covalently capture an acquired cysteine in K-Ras-G12C mutation and lock it in a signaling-incompetent state. However, covalent inhibition of G12D, the most frequent K-Ras mutation particularly prevalent in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, has remained elusive due to the lack of aspartate-targeting chemistry. Here we present a set of malolactone-based electrophiles that exploit ring strain to crosslink K-Ras-G12D at the mutant aspartate to form stable covalent complexes. Structural insights from X-ray crystallography and exploitation of the stereoelectronic requirements for attack of the electrophile allowed development of a substituted malolactone that resisted attack by aqueous buffer but rapidly crosslinked with the aspartate-12 of K-Ras in both GDP and GTP state. The GTP-state targeting allowed effective suppression of downstream signaling, and selective inhibition of K-Ras-G12D-driven cancer cell proliferation in vitro and xenograft growth in mice.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA.