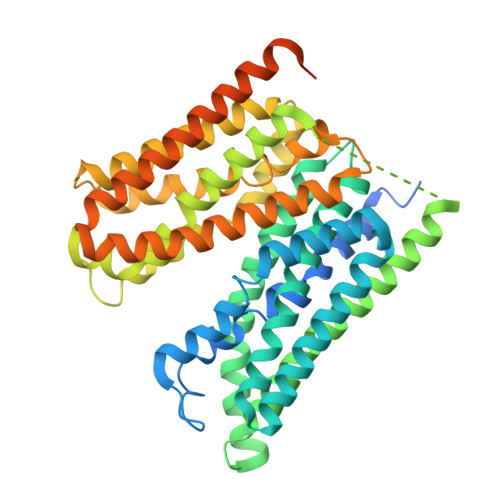
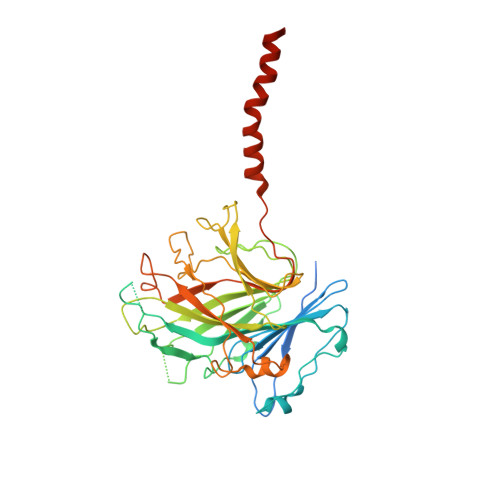
MFSD1 with its accessory subunit GLMP functions as a general dipeptide uniporter in lysosomes.
Jungnickel, K.E.J., Guelle, O., Iguchi, M., Dong, W., Kotov, V., Gabriel, F., Debacker, C., Dairou, J., McCort-Tranchepain, I., Laqtom, N.N., Chan, S.H., Ejima, A., Sato, K., Massa Lopez, D., Saftig, P., Mehdipour, A.R., Abu-Remaileh, M., Gasnier, B., Low, C., Damme, M.(2024) Nat Cell Biol
- PubMed: 38839979
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-024-01436-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8R8Q - PubMed Abstract:
The lysosomal degradation of macromolecules produces diverse small metabolites exported by specific transporters for reuse in biosynthetic pathways. Here we deorphanized the major facilitator superfamily domain containing 1 (MFSD1) protein, which forms a tight complex with the glycosylated lysosomal membrane protein (GLMP) in the lysosomal membrane. Untargeted metabolomics analysis of MFSD1-deficient mouse lysosomes revealed an increase in cationic dipeptides. Purified MFSD1 selectively bound diverse dipeptides, while electrophysiological, isotope tracer and fluorescence-based studies in Xenopus oocytes and proteoliposomes showed that MFSD1-GLMP acts as a uniporter for cationic, neutral and anionic dipeptides. Cryoelectron microscopy structure of the dipeptide-bound MFSD1-GLMP complex in outward-open conformation characterized the heterodimer interface and, in combination with molecular dynamics simulations, provided a structural basis for its selectivity towards diverse dipeptides. Together, our data identify MFSD1 as a general lysosomal dipeptide uniporter, providing an alternative route to recycle lysosomal proteolysis products when lysosomal amino acid exporters are overloaded.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Structural Systems Biology, Hamburg, Germany.