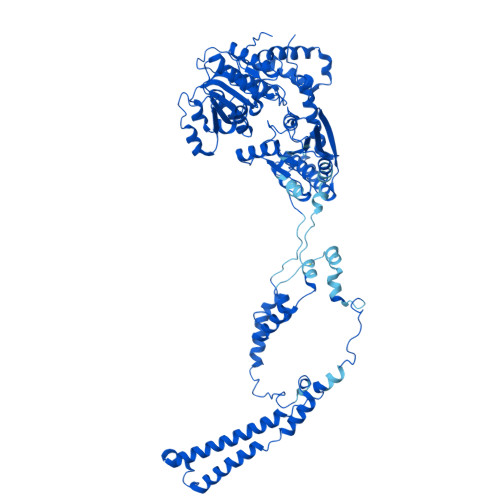
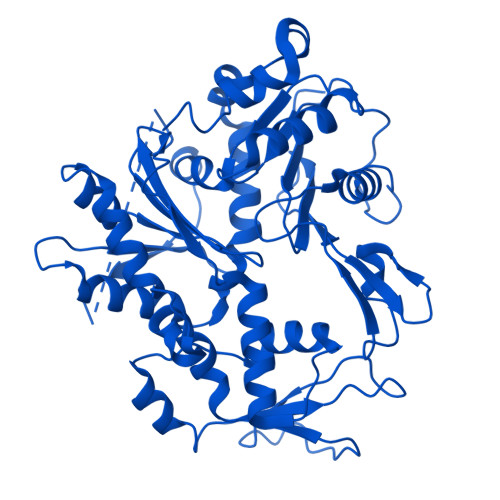
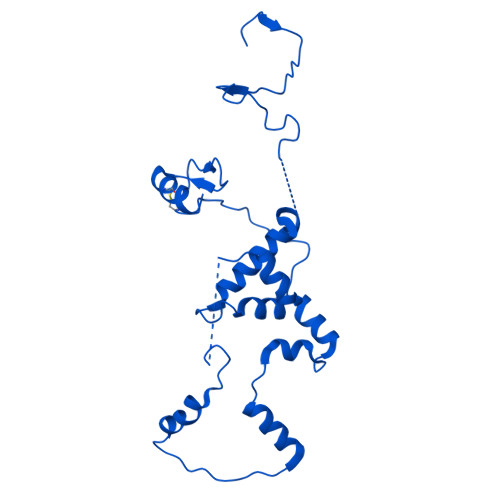
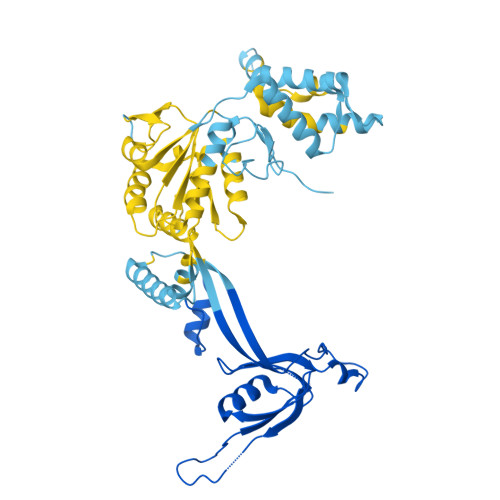
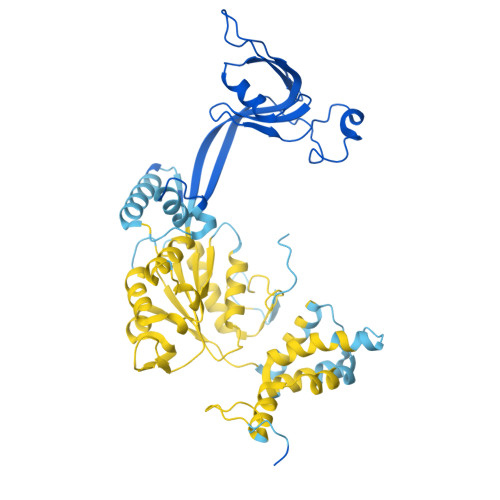
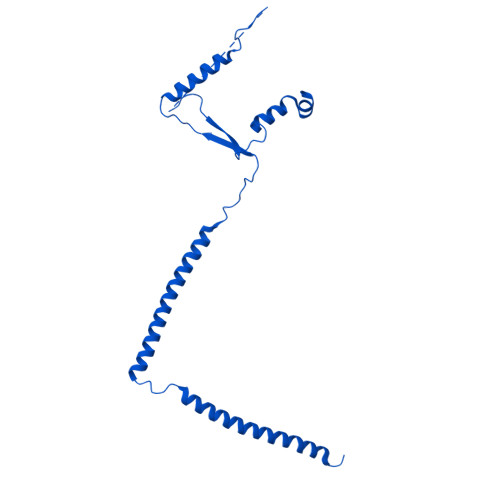
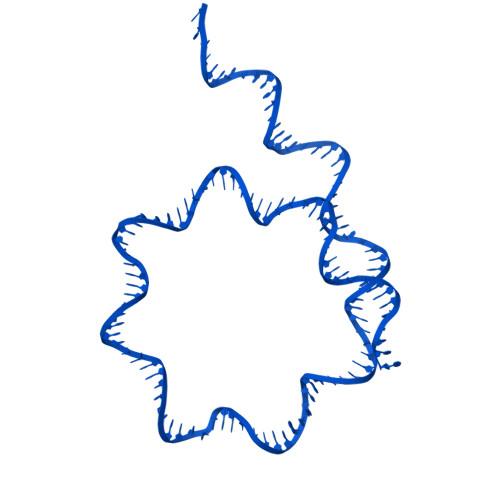
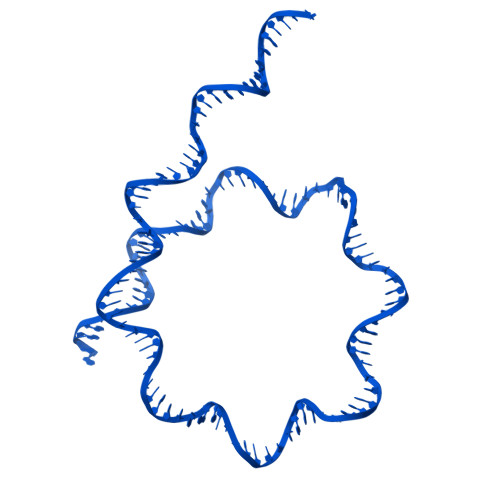
Stabilization of the hexasome intermediate during histone exchange by yeast SWR1 complex.
Jalal, A.S.B., Girvan, P., Chua, E.Y.D., Liu, L., Wang, S., McCormack, E.A., Skehan, M.T., Knight, C.L., Rueda, D.S., Wigley, D.B.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 3871
- PubMed: 39226902
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.08.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QYV, 8QZ0, 9FBW - PubMed Abstract:
The yeast SWR1 complex catalyzes the exchange of histone H2A/H2B dimers in nucleosomes with Htz1/H2B dimers. We use cryoelectron microscopy to determine the structure of an enzyme-bound hexasome intermediate in the reaction pathway of histone exchange, in which an H2A/H2B dimer has been extracted from a nucleosome prior to the insertion of a dimer comprising Htz1/H2B. The structure reveals a key role for the Swc5 subunit in stabilizing the unwrapping of DNA from the histone core of the hexasome. By engineering a crosslink between an Htz1/H2B dimer and its chaperone protein Chz1, we show that this blocks histone exchange by SWR1 but allows the incoming chaperone-dimer complex to insert into the hexasome. We use this reagent to trap an SWR1/hexasome complex with an incoming Htz1/H2B dimer that shows how the reaction progresses to the next step. Taken together the structures reveal insights into the mechanism of histone exchange by SWR1 complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Section of Structural Biology, Department Infectious Disease, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK.