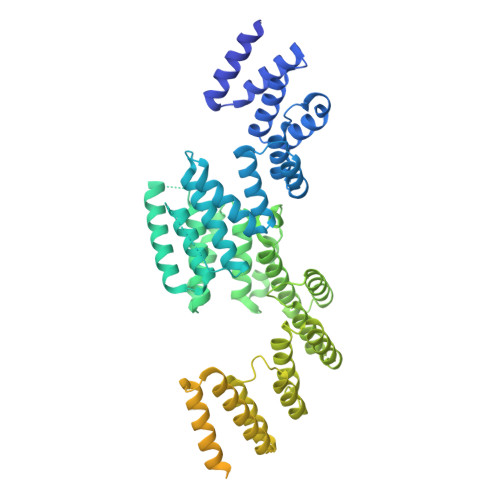
Cryo-EM structure of SRP68/72 reveals an extended dimerization domain with RNA-binding activity.
Zhong, Y., Feng, J., Koh, A.F., Kotecha, A., Greber, B.J., Ataide, S.F.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 5285-5300
- PubMed: 38366771
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QVW - PubMed Abstract:
The signal recognition particle (SRP) is a critical component in protein sorting pathways in all domains of life. Human SRP contains six proteins bound to the 7S RNA and their structures and functions have been mostly elucidated. The SRP68/72 dimer is the largest SRP component and is essential for SRP function. Although the structures of the SRP68/72 RNA binding and dimerization domains have been previously reported, the structure and function of large portions of the SRP68/72 dimer remain unknown. Here, we analyse full-length SRP68/72 using cryo-EM and report that SRP68/72 depend on each other for stability and form an extended dimerization domain. This newly observed dimerization domain is both a protein- and RNA-binding domain. Comparative analysis with current structural models suggests that this dimerization domain undergoes dramatic translocation upon SRP docking onto SRP receptor and eventually comes close to the Alu domain. We propose that the SRP68/72 dimerization domain functions by binding and detaching the Alu domain and SRP9/14 from the ribosomal surface, thus releasing elongation arrest upon docking onto the ER membrane.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, The University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia.