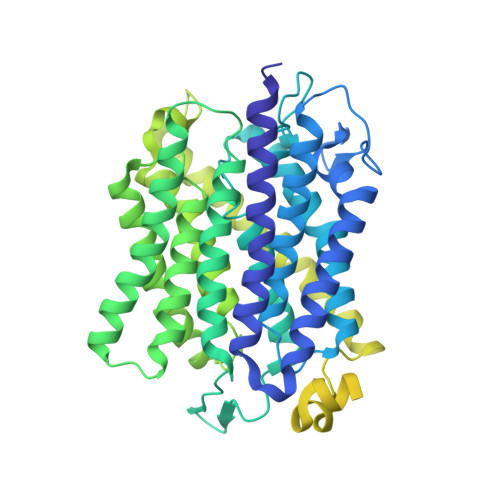
How sensor Amt-like proteins integrate ammonium signals.
Pfluger, T., Gschell, M., Zhang, L., Shnitsar, V., Zabadne, A.J., Zierep, P., Gunther, S., Einsle, O., Andrade, S.L.A.(2024) Sci Adv 10: eadm9441-eadm9441
- PubMed: 38838143
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adm9441
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QJ3, 8QJ4, 8QPF - PubMed Abstract:
Unlike aquaporins or potassium channels, ammonium transporters (Amts) uniquely discriminate ammonium from potassium and water. This feature has certainly contributed to their repurposing as ammonium receptors during evolution. Here, we describe the ammonium receptor Sd-Amt1, where an Amt module connects to a cytoplasmic diguanylate cyclase transducer module via an HAMP domain. Structures of the protein with and without bound ammonium were determined to 1.7- and 1.9-Ångstrom resolution, depicting the ON and OFF states of the receptor and confirming the presence of a binding site for two ammonium cations that is pivotal for signal perception and receptor activation. The transducer domain was disordered in the crystals, and an AlphaFold2 prediction suggests that the helices linking both domains are flexible. While the sensor domain retains the trimeric fold formed by all Amt family members, the HAMP domains interact as pairs and serve to dimerize the transducer domain upon activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy, Institute for Biochemistry, University Freiburg, Albertstr. 21, 79104 Freiburg, Germany.