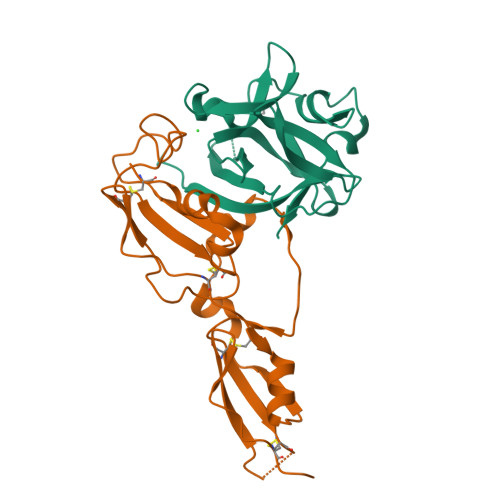
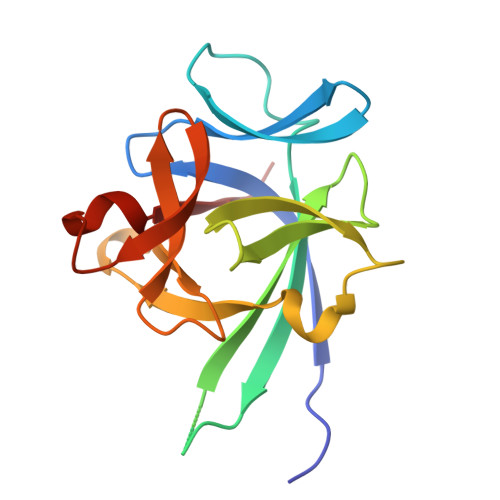
Structural basis for IL-33 recognition and its antagonism by the helminth effector protein HpARI2.
Jamwal, A., Colomb, F., McSorley, H.J., Higgins, M.K.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 5226-5226
- PubMed: 38890291
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49550-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Q5R - PubMed Abstract:
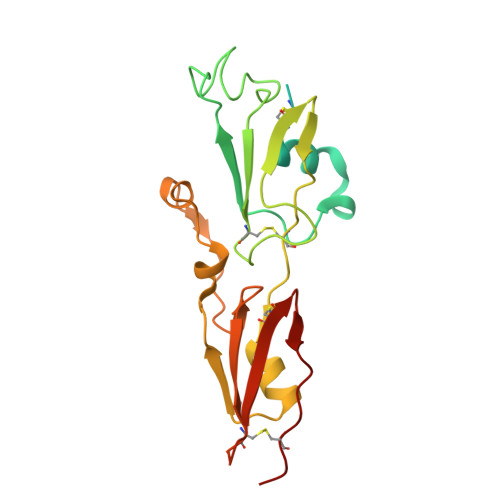
IL-33 plays a significant role in inflammation, allergy, and host defence against parasitic helminths. The model gastrointestinal nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri secretes the Alarmin Release Inhibitor HpARI2, an effector protein that suppresses protective immune responses and asthma in its host by inhibiting IL-33 signalling. Here we reveal the structure of HpARI2 bound to mouse IL-33. HpARI2 contains three CCP-like domains, and we show that it contacts IL-33 primarily through the second and third of these. A large loop which emerges from CCP3 directly contacts IL-33 and structural comparison shows that this overlaps with the binding site on IL-33 for its receptor, ST2, preventing formation of a signalling complex. Truncations of HpARI2 which lack the large loop from CCP3 are not able to block IL-33-mediated signalling in a cell-based assay and in an in vivo female mouse model of asthma. This shows that direct competition between HpARI2 and ST2 is responsible for suppression of IL-33-dependent responses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford, OX1 3QU, UK.