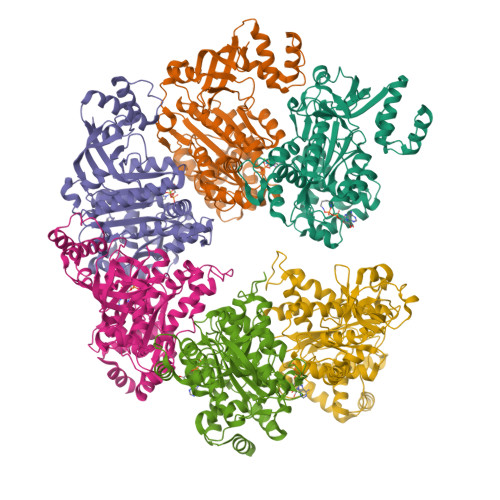
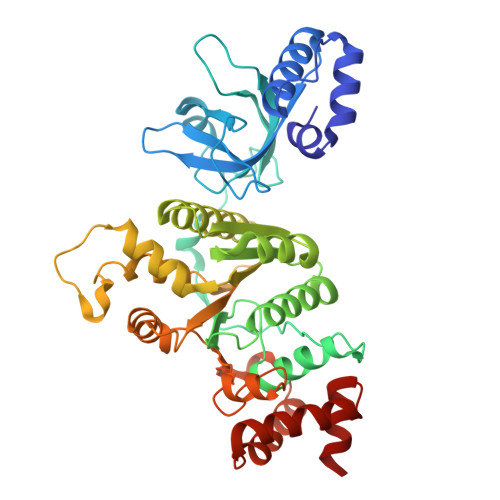
Transcription termination factor rho polymerizes under stress.
Wang, B., Said, N., Hilal, T., Finazzo, M., Wahl, M.C., Artsimovitch, I.(2023) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 37645988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.18.553922
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Q3N, 8Q3O, 8Q3P, 8Q3Q - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial RNA helicase ρ is a genome sentinel that terminates synthesis of damaged and junk RNAs that are not translated by the ribosome. Co-transcriptional RNA surveillance by ρ is essential for quality control of the transcriptome during optimal growth. However, it is unclear how bacteria protect their RNAs from overzealous ρ during dormancy or stress, conditions common in natural habitats. Here we used cryogenic electron microscopy, biochemical, and genetic approaches to show that residue substitutions, ADP, or ppGpp promote hyper-oligomerization of Escherichia coli ρ. Our results demonstrate that nucleotides bound at subunit interfaces control ρ switching from active hexamers to inactive higher-order oligomers and extended filaments. Polymers formed upon exposure to antibiotics or ppGpp disassemble when stress is relieved, thereby directly linking termination activity to cellular physiology. Inactivation of ρ through hyper-oligomerization is a regulatory strategy shared by RNA polymerases, ribosomes, and metabolic enzymes across all life.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Center for RNA Biology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA.