Structural insights into the N-terminal APHB domain of HrpA: mediating canonical and i-motif recognition.
Xin, B.G., Huang, L.Y., Yuan, L.G., Liu, N.N., Li, H.H., Ai, X., Lei, D.S., Hou, X.M., Rety, S., Xi, X.G.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 3406-3418
- PubMed: 38412313
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae138
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8PO6, 8PO7, 8PO8 - PubMed Abstract:
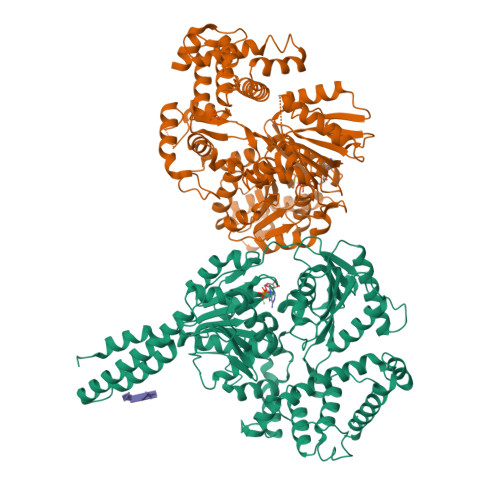
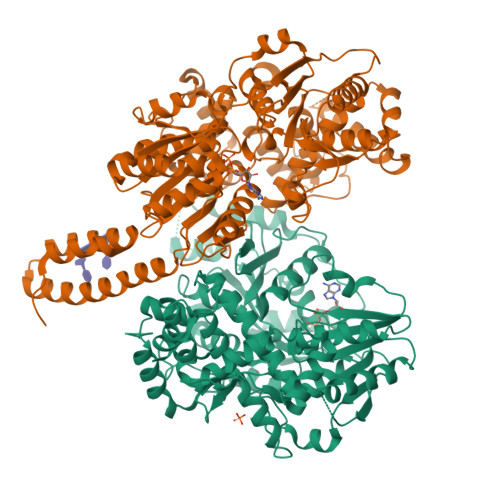
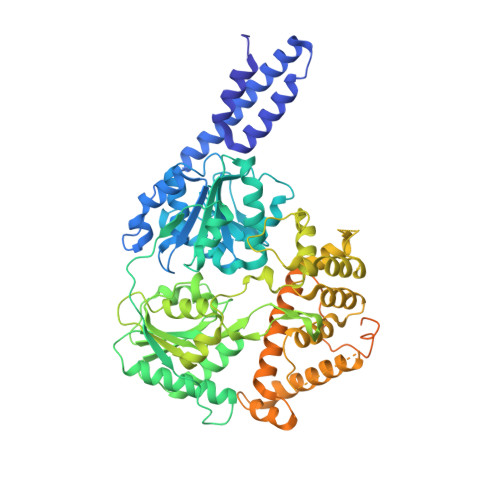
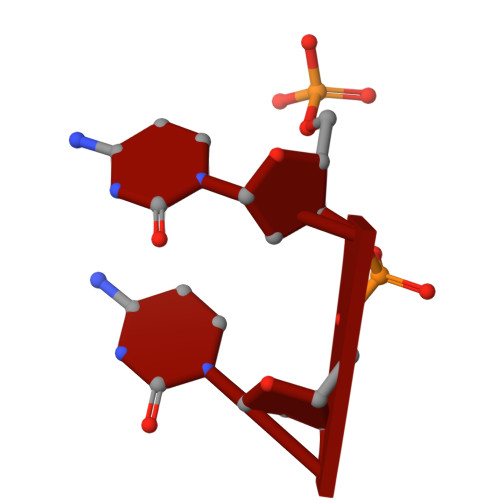
RNA helicases function as versatile enzymes primarily responsible for remodeling RNA secondary structures and organizing ribonucleoprotein complexes. In our study, we conducted a systematic analysis of the helicase-related activities of Escherichia coli HrpA and presented the structures of both its apo form and its complex bound with both conventional and non-canonical DNAs. Our findings reveal that HrpA exhibits NTP hydrolysis activity and binds to ssDNA and ssRNA in distinct sequence-dependent manners. While the helicase core plays an essential role in unwinding RNA/RNA and RNA/DNA duplexes, the N-terminal extension in HrpA, consisting of three helices referred to as the APHB domain, is crucial for ssDNA binding and RNA/DNA duplex unwinding. Importantly, the APHB domain is implicated in binding to non-canonical DNA structures such as G-quadruplex and i-motif, and this report presents the first solved i-motif-helicase complex. This research not only provides comprehensive insights into the multifaceted roles of HrpA as an RNA helicase but also establishes a foundation for further investigations into the recognition and functional implications of i-motif DNA structures in various biological processes.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Life Sciences, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China.