Reverse-engineering the anti-MUC1 antibody 139H2 by mass spectrometry-based de novo sequencing.
Peng, W., Giesbers, K.C., Siborova, M., Beugelink, J.W., Pronker, M.F., Schulte, D., Hilkens, J., Janssen, B.J., Strijbis, K., Snijder, J.(2024) Life Sci Alliance 7
- PubMed: 38508723
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202302366
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8P6I - PubMed Abstract:
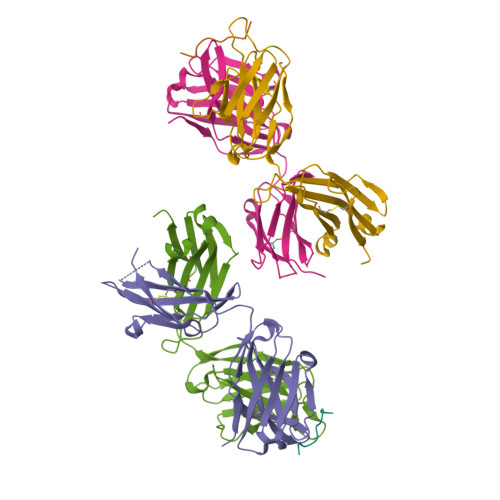
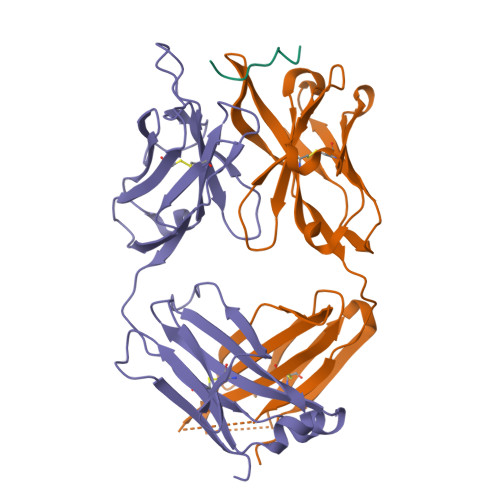
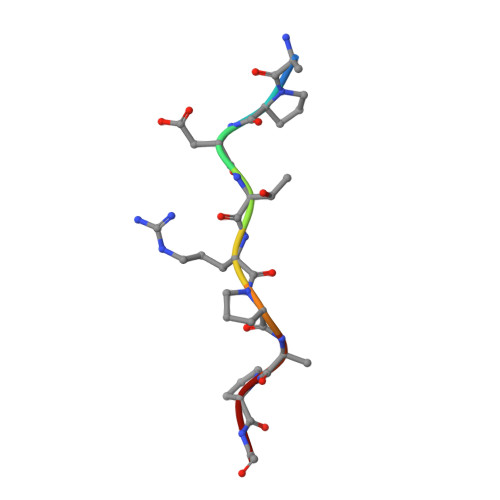
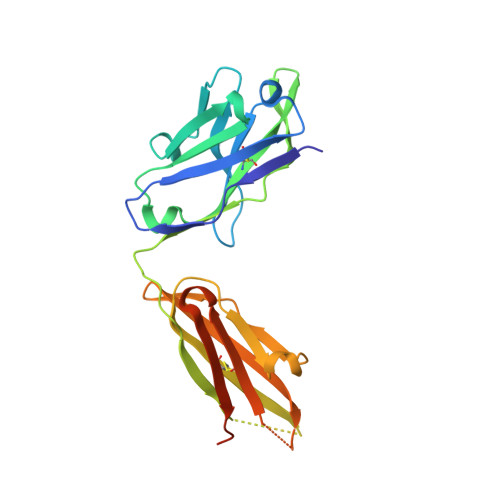
Mucin 1 (MUC1) is a transmembrane mucin expressed at the apical surface of epithelial cells at mucosal surfaces. MUC1 has a barrier function against bacterial invasion and is well known for its aberrant expression and glycosylation in adenocarcinomas. The MUC1 extracellular domain contains a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) of 20 amino acids, which are heavily O -linked glycosylated. Monoclonal antibodies against the MUC1 VNTR are powerful research tools with applications in the diagnosis and treatment of MUC1-expressing cancers. Here, we report direct mass spectrometry-based sequencing of anti-MUC1 hybridoma-derived 139H2 IgG, enabling reverse-engineering of the functional recombinant monoclonal antibody. The crystal structure of the 139H2 Fab fragment in complex with the MUC1 epitope was solved, revealing the molecular basis of 139H2 binding specificity to MUC1 and its tolerance to O -glycosylation of the VNTR. The available sequence of 139H2 will allow further development of MUC1-related diagnostic, targeting, and treatment strategies.
Organizational Affiliation:
https://ror.org/04pp8hn57 Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics, Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research and Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands.