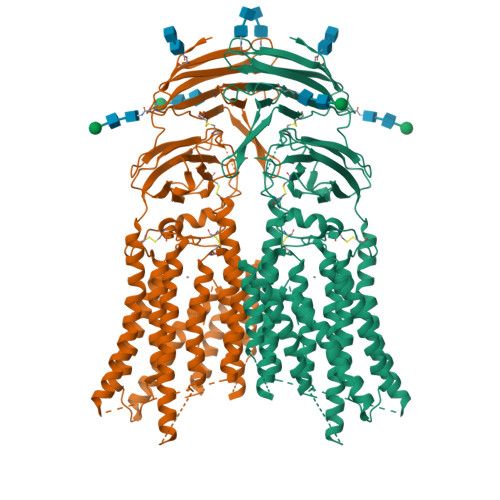
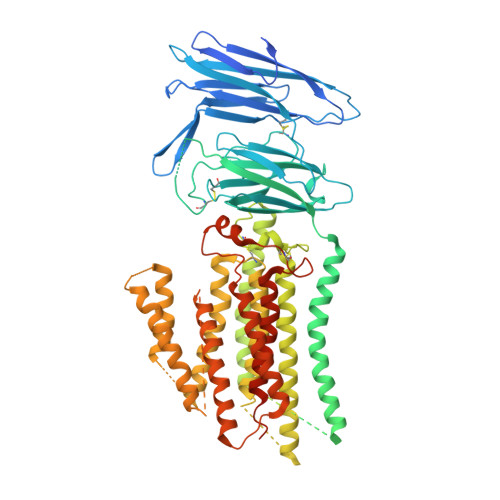
Cryo-EM analysis reveals human SID-1 transmembrane family member 1 dynamics underlying lipid hydrolytic activity.
Hirano, Y., Ohto, U., Ichi, I., Sato, R., Miyake, K., Shimizu, T.(2024) Commun Biol 7: 664-664
- PubMed: 38811802
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-024-06346-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8KCW, 8KCX - PubMed Abstract:
Two mammalian homologs of systemic RNA interference defective protein 1 (SID-1) (SIDT1/2) are suggested to function as double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) transporters for extracellular dsRNA uptake or for release of incorporated dsRNA from lysosome to cytoplasm. SIDT1/2 is also suggested to be involved in cholesterol transport and lipid metabolism. Here, we determine the cryo-electron microscopy structures of human SIDT1, homodimer in a side-by-side arrangement, with two distinct conformations, the cholesterol-bound form and the unbound form. Our structures reveal that the membrane-spanning region of SIDT1 harbors conserved histidine and aspartate residues coordinating to putative zinc ion, in a structurally similar manner to alkaline ceramidases or adiponectin receptors that require zinc for ceramidase activity. We identify that SIDT1 has a ceramidase activity that is attenuated by cholesterol binding. Observations from two structures suggest that cholesterol molecules serve as allosteric regulator that binds the transmembrane region of SIDT1 and induces the conformation change and the reorientation of the catalytic residues. This study represents a contribution to the elucidation of the cholesterol-mediated mechanisms of lipid hydrolytic activity and RNA transport in the SID-1 family proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan.