Structural basis of ligand recognition and design of antihistamines targeting histamine H 4 receptor.
Xia, R., Shi, S., Xu, Z., Vischer, H.F., Windhorst, A.D., Qian, Y., Duan, Y., Liang, J., Chen, K., Zhang, A., Guo, C., Leurs, R., He, Y.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 2493-2493
- PubMed: 38509098
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46840-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JXT, 8JXV, 8JXW, 8JXX - PubMed Abstract:
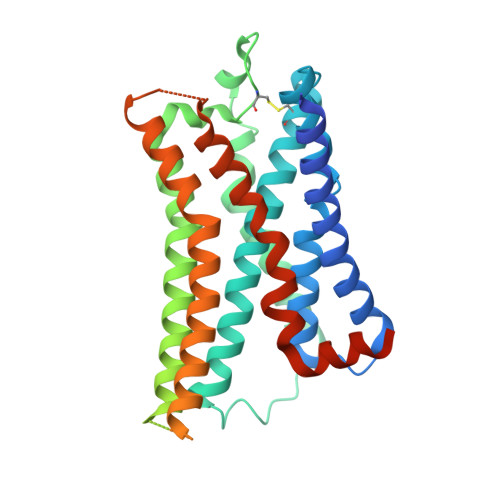
The histamine H 4 receptor (H 4 R) plays key role in immune cell function and is a highly valued target for treating allergic and inflammatory diseases. However, structural information of H 4 R remains elusive. Here, we report four cryo-EM structures of H 4 R/G i complexes, with either histamine or synthetic agonists clobenpropit, VUF6884 and clozapine bound. Combined with mutagenesis, ligand binding and functional assays, the structural data reveal a distinct ligand binding mode where D94 3.32 and a π-π network determine the orientation of the positively charged group of ligands, while E182 5.46 , located at the opposite end of the ligand binding pocket, plays a key role in regulating receptor activity. The structural insight into H 4 R ligand binding allows us to identify mutants at E182 5.46 for which the agonist clobenpropit acts as an inverse agonist and to correctly predict inverse agonism of a closely related analog with nanomolar potency. Together with the findings regarding receptor activation and G i engagement, we establish a framework for understanding H 4 R signaling and provide a rational basis for designing novel antihistamines targeting H 4 R.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Receptor Structure and Signaling, HIT Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China.