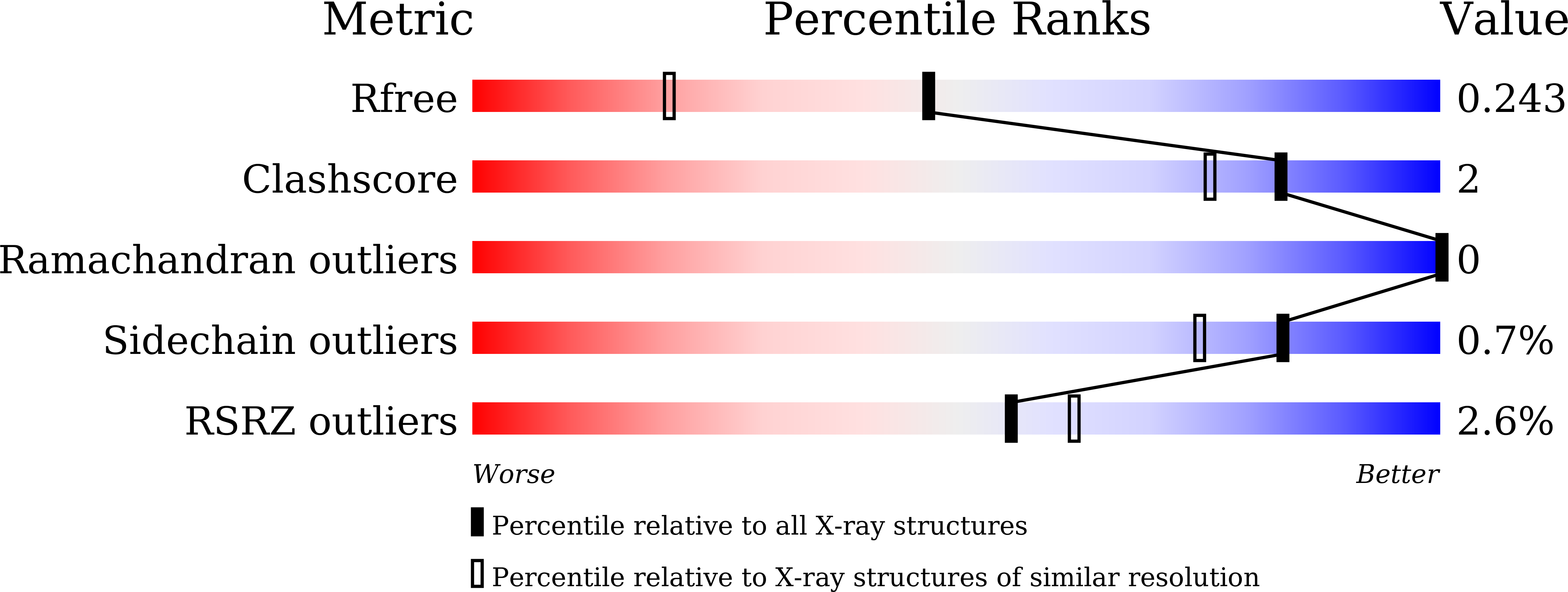
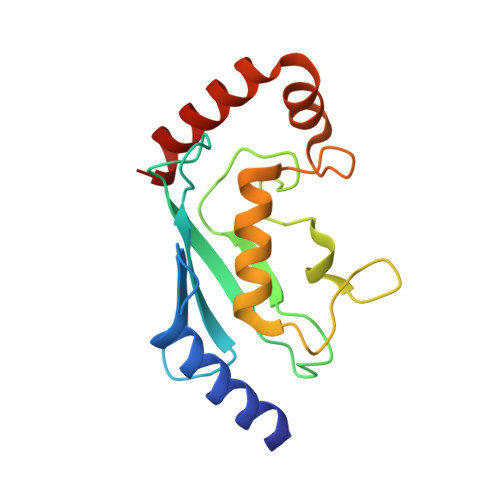
Identification and characterization of inhibitors covalently modifying catalytic cysteine of UBE2T and blocking ubiquitin transfer.
Anantharajan, J., Tan, Q.W., Fulwood, J., Sifang, W., Huang, Q., Ng, H.Q., Koh, X., Xu, W., Cherian, J., Baburajendran, N., Kang, C., Ke, Z.(2023) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 689: 149238-149238
- PubMed: 37979329
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.149238
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JVE, 8JVL - PubMed Abstract:
UBE2T is an E2 ubiquitin ligase critical for ubiquitination of substrate and plays important roles in many diseases. Despite the important function, UBE2T is considered as an undruggable target due to lack of a pocket for binding to small molecules with satisfied properties for clinical applications. To develop potent and specific UBE2T inhibitors, we adopted a high-throughput screening assay and two compounds-ETC-6152 and ETC-9004 containing a sulfone tetrazole scaffold were identified. Solution NMR study demonstrated the direct interactions between UBE2T and compounds in solution. Further co-crystal structures reveal the binding modes of these compounds. Both compound hydrolysation and formation of a hydrogen bond with the thiol group of the catalytic cysteine were observed. The formation of covalent complex was confirmed with mass spectrometry. As these two compounds inhibit ubiquitin transfer, our study provides a strategy to develop potent inhibitors of UBE2T.
Organizational Affiliation:
Experimental Drug Development Centre (EDDC), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), 10 Biopolis Road, #5-01, 138670, Singapore.