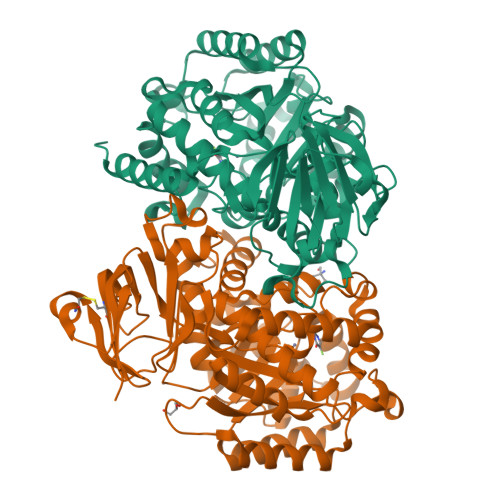
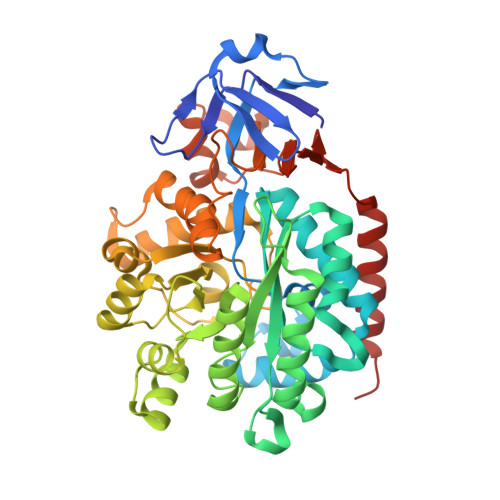
Structural characterization of an isocytosine-specific deaminase VCZ reveals its application potential in the anti-cancer therapy.
Guo, W., Li, X., Fan, J., Li, H., Wen, Y., Meng, C., Chen, H., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Y., Du, Y., Wu, B.(2023) iScience 26: 107672-107672
- PubMed: 37680460
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2023.107672
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WW2, 8IS4, 8IS5 - PubMed Abstract:
Non-natural nucleobase isocytosine (IC) is the isomer of cytosine; its chemical derivate 5-fluoroisocytosine (5-FIC) together with the isocytosine-specific deaminase (ICD) VCZ was suggested to be potential practical enzyme/prodrug pair for cancer therapy through gene-directed enzyme-prodrug therapy (GDEPT) method. In this study, we have determined the crystal structures of apo-VCZ and its complex with 5-FU. We identified the critical residues for substrate binding and catalytic reaction. We also captured the substrate-induced conformational changes of VCZ, then proposed the conjectural reaction procedures of VCZ for converting the IC into the uracil. Moreover, we evaluated the therapeutic effect of wildtype or the mutated VCZ protein in the colorectal cancer cell lines. Our studies will shed light on optimizing the ICD/5-FIC pairs by modifying either the enzyme or the prodrug based on the structural observations, thereby improving the possibility of applying the ICD/5-FIC pair in clinical trials.
Organizational Affiliation:
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Epigenetics and Gene Regulation, Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for RNA Medicine, Medical Research Center, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China.