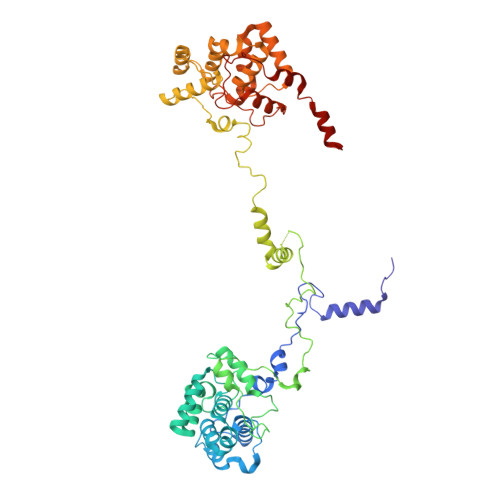
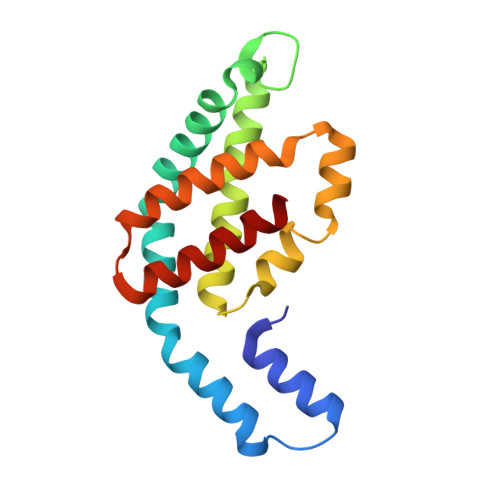
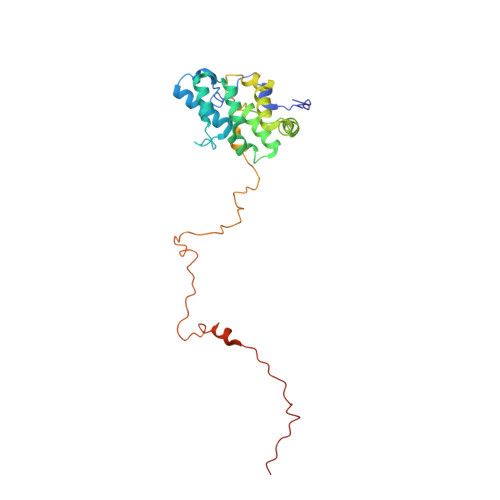
A structure of the relict phycobilisome from a thylakoid-free cyanobacterium.
Jiang, H.W., Wu, H.Y., Wang, C.H., Yang, C.H., Ko, J.T., Ho, H.C., Tsai, M.D., Bryant, D.A., Li, F.W., Ho, M.C., Ho, M.Y.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 8009-8009
- PubMed: 38049400
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43646-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8IMI, 8IMJ, 8IMK, 8IML, 8IMM, 8IMN, 8IMO - PubMed Abstract:
Phycobilisomes (PBS) are antenna megacomplexes that transfer energy to photosystems II and I in thylakoids. PBS likely evolved from a basic, inefficient form into the predominant hemidiscoidal shape with radiating peripheral rods. However, it has been challenging to test this hypothesis because ancestral species are generally inaccessible. Here we use spectroscopy and cryo-electron microscopy to reveal a structure of a "paddle-shaped" PBS from a thylakoid-free cyanobacterium that likely retains ancestral traits. This PBS lacks rods and specialized ApcD and ApcF subunits, indicating relict characteristics. Other features include linkers connecting two chains of five phycocyanin hexamers (CpcN) and two core subdomains (ApcH), resulting in a paddle-shaped configuration. Energy transfer calculations demonstrate that chains are less efficient than rods. These features may nevertheless have increased light absorption by elongating PBS before multilayered thylakoids with hemidiscoidal PBS evolved. Our results provide insights into the evolution and diversification of light-harvesting strategies before the origin of thylakoids.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Life Science, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.