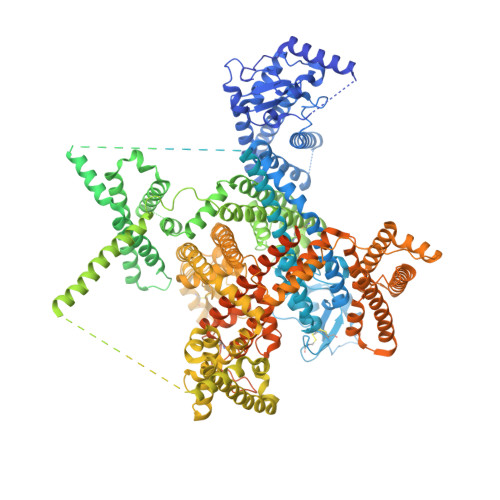
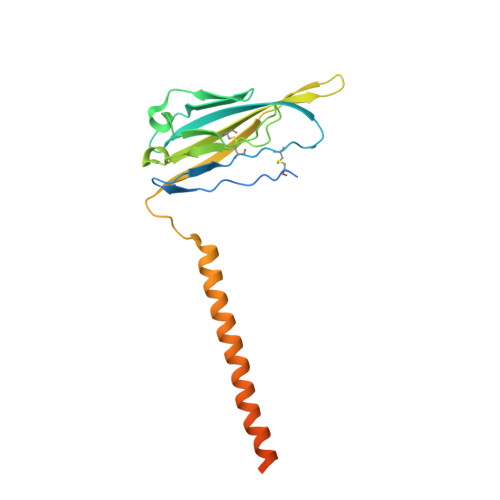
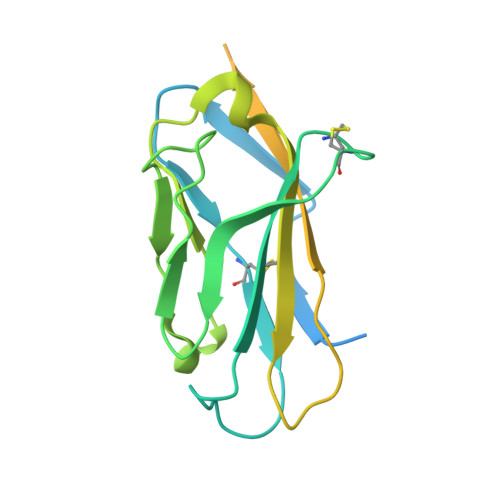
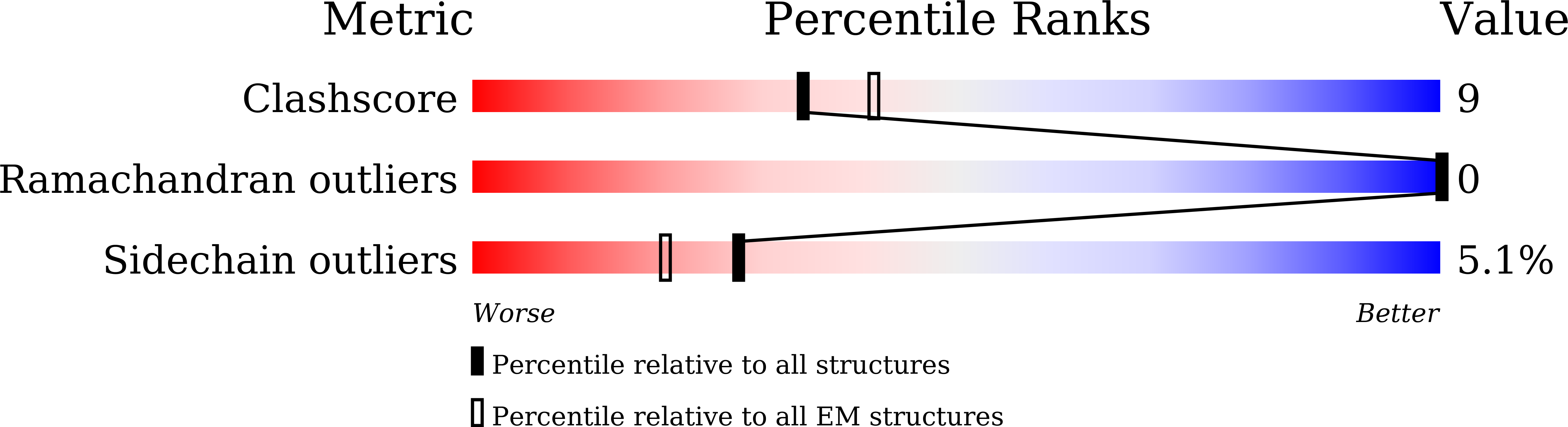Structural mapping of Na v 1.7 antagonists.
Wu, Q., Huang, J., Fan, X., Wang, K., Jin, X., Huang, G., Li, J., Pan, X., Yan, N.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 3224-3224
- PubMed: 37270609
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38942-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I5B, 8I5G, 8I5X, 8I5Y, 8J4F, 8S9B, 8S9C - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated sodium (Na v ) channels are targeted by a number of widely used and investigational drugs for the treatment of epilepsy, arrhythmia, pain, and other disorders. Despite recent advances in structural elucidation of Na v channels, the binding mode of most Na v -targeting drugs remains unknown. Here we report high-resolution cryo-EM structures of human Na v 1.7 treated with drugs and lead compounds with representative chemical backbones at resolutions of 2.6-3.2 Å. A binding site beneath the intracellular gate (site BIG) accommodates carbamazepine, bupivacaine, and lacosamide. Unexpectedly, a second molecule of lacosamide plugs into the selectivity filter from the central cavity. Fenestrations are popular sites for various state-dependent drugs. We show that vinpocetine, a synthetic derivative of a vinca alkaloid, and hardwickiic acid, a natural product with antinociceptive effect, bind to the III-IV fenestration, while vixotrigine, an analgesic candidate, penetrates the IV-I fenestration of the pore domain. Our results permit building a 3D structural map for known drug-binding sites on Na v channels summarized from the present and previous structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structures, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China.