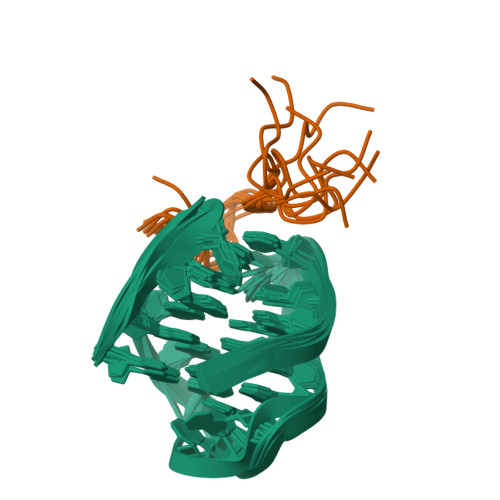
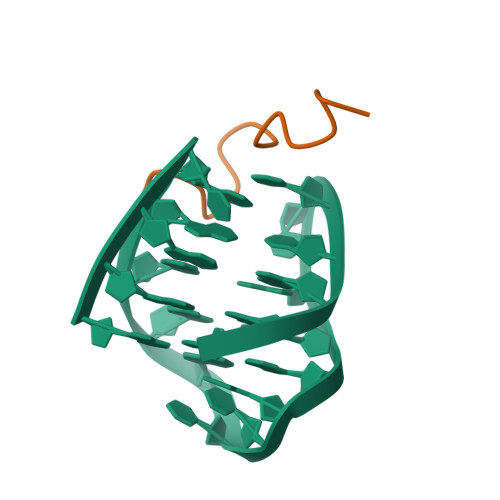
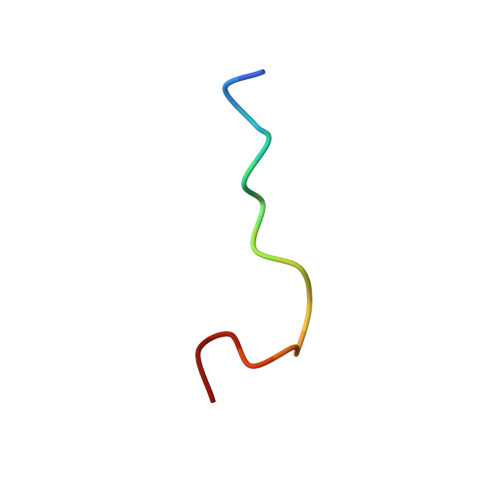
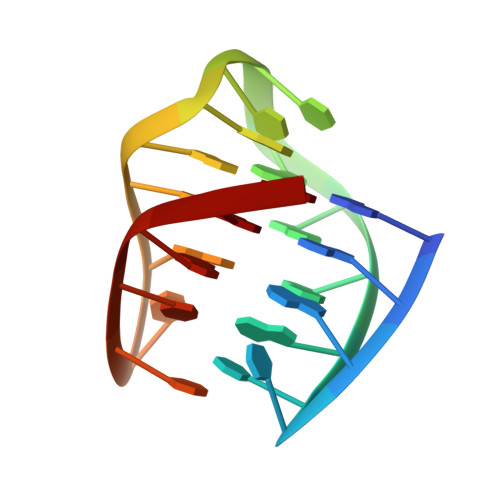
The N-terminal region of Cdc6 specifically recognizes human DNA G-quadruplex.
Geng, Y., Liu, C., Xu, N., Shi, X., Suen, M.C., Zhou, B., Yan, B., Wu, C., Li, H., Song, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Z., Cai, Q., Zhu, G.(2024) Int J Biol Macromol 260: 129487-129487
- PubMed: 38237821
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129487
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HT7 - PubMed Abstract:
Guanine (G)-rich nucleic acid sequences can form diverse G-quadruplex structures located in functionally significant genome regions, exerting regulatory control over essential biological processes, including DNA replication in vivo. During the initiation of DNA replication, Cdc6 is recruited by the origin recognition complex (ORC) to target specific chromosomal DNA sequences. This study reveals that human Cdc6 interacts with G-quadruplex structure through a distinct region within the N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR), encompassing residues 7-20. The binding region assumes a hook-type conformation, as elucidated by the NMR solution structure in complex with htel21T 18 . Significantly, mutagenesis and in vivo investigations confirm the highly specific nature of Cdc6's recognition of G-quadruplex. This research enhances our understanding of the fundamental mechanism governing the interaction between G-quadruplex and the N-terminal IDR region of Cdc6, shedding light on the intricate regulation of DNA replication processes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Clinical Research Institute of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Fujian Key Laboratory of Brain Tumors Diagnosis and Precision Treatment, Xiamen Key Laboratory of Brain Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China; Institute for Advanced Study and State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Division of Life Science, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong.