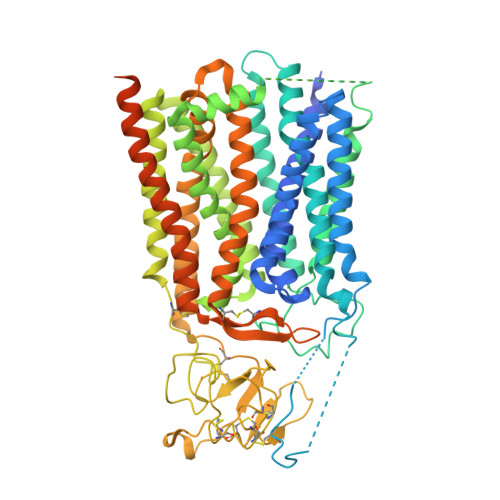
Cryo-EM structures of human organic anion transporting polypeptide OATP1B1.
Shan, Z., Yang, X., Liu, H., Yuan, Y., Xiao, Y., Nan, J., Zhang, W., Song, W., Wang, J., Wei, F., Zhang, Y.(2023) Cell Res 33: 940-951
- PubMed: 37674011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-023-00870-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HNB, 8HNC, 8HND, 8HNH, 8K6L - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the solute carrier organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATPs) family function as transporters for a large variety of amphipathic organic anions including endogenous metabolites and clinical drugs, such as bile salts, steroids, thyroid hormones, statins, antibiotics, antivirals, and anticancer drugs. OATP1B1 plays a vital role in transporting such substances into the liver for hepatic clearance. FDA and EMA recommend conducting in vitro testing of drug-drug interactions (DDIs) involving OATP1B1. However, the structure and working mechanism of OATPs still remains elusive. In this study, we determined cryo-EM structures of human OATP1B1 bound with representative endogenous metabolites (bilirubin and estrone-3-sulfate), a clinical drug (simeprevir), and a fluorescent indicator (2',7'-dichlorofluorescein), in both outward- and inward-open states. These structures reveal major and minor substrate binding pockets and conformational changes during transport. In combination with mutagenesis studies and molecular dynamics simulations, our work comprehensively elucidates the transport mechanism of OATP1B1 and provides the structural basis for DDI predictions involving OATP1B1, which will greatly promote our understanding of OATPs.
- Shanghai Fifth People's Hospital, Fudan University, and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Medical Epigenetics, International Co-laboratory of Medical Epigenetics and Metabolism (Ministry of Science and Technology), Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: