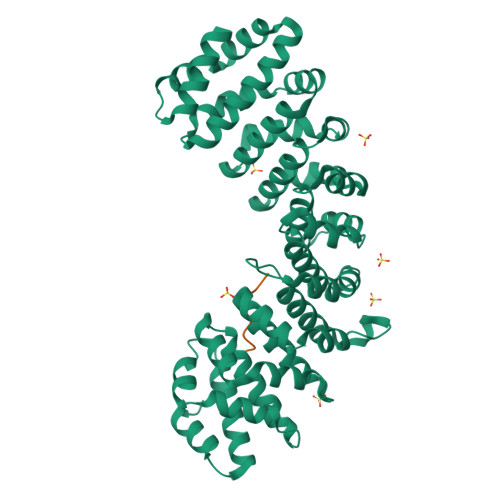
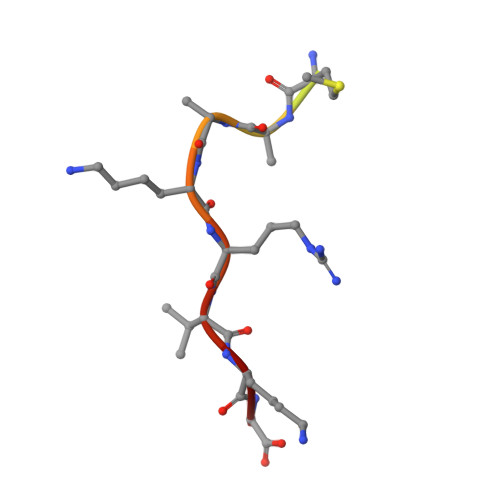
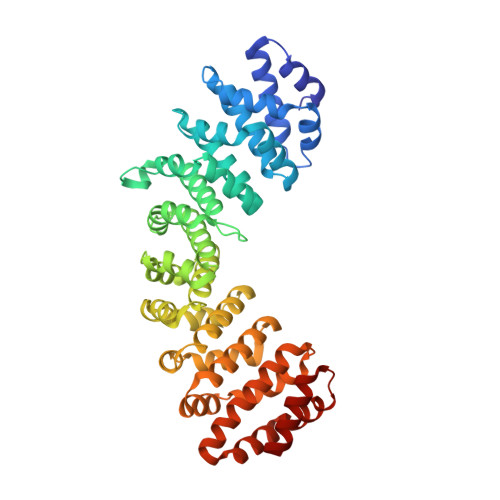Structures of importin-alpha bound to the wild-type and an internal deletion mutant of the bipartite nuclear localization signal of HIF-1 alpha.
Matsuura, Y., Miyawaki, K.(2023) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 652: 1-5
- PubMed: 36806083
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.02.036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HE0, 8HE3 - PubMed Abstract:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) is a heterodimeric transcription factor that plays an important role as a master regulator of oxygen homeostasis. The activity of HIF-1 is regulated in part by dynamic intracellular trafficking of its α subunit (HIF-1α) that can shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm. It has been shown that nuclear localization of HIF-1α requires a variant of classic nuclear localization signal (NLS) and that an internal deletion of the amino acid residues (residues 724-751) in the NLS almost abolish the nuclear localization. Here we report the X-ray crystal structure of the nuclear import adaptor importin-α1 bound to the wild-type HIF-1α NLS at 1.8 Å resolution and of importin-α1 bound to the Δ724-751 mutant of the HIF-1α NLS at 1.9 Å resolution. In the wild-type structure, two basic clusters in the HIF-1α NLS made extensive interactions with importin-α1 on two sites (the major site and the minor site). In the mutant structure, the NLS residues still interacted extensively with the major site on importin-α1, but the interactions with the minor site were not observed. The structural data, together with computational analyses of binding free energies, indicate that the loss of the minor-site interactions inhibit nuclear accumulation of HIF-1α.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, International University of Health and Welfare, Japan; Division of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Japan. Electronic address: ymatsuura@iuhw.ac.jp.