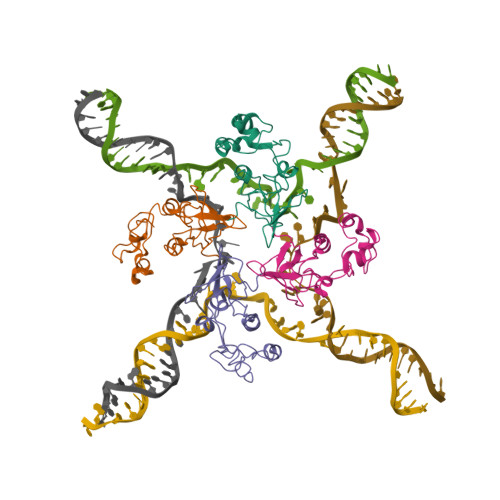
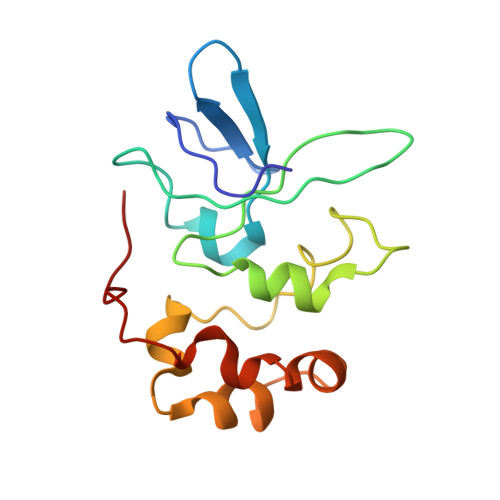
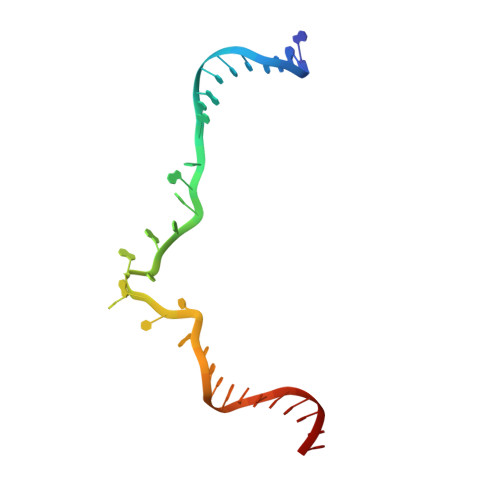
Molecular mechanisms of Holliday junction branch migration catalyzed by an asymmetric RuvB hexamer.
Rish, A.D., Shen, Z., Chen, Z., Zhang, N., Zheng, Q., Fu, T.M.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 3549-3549
- PubMed: 37322069
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39250-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EFV, 8EFY, 8GH8 - PubMed Abstract:
The Holliday junction (HJ) is a DNA intermediate of homologous recombination, involved in many fundamental physiological processes. RuvB, an ATPase motor protein, drives branch migration of the Holliday junction with a mechanism that had yet to be elucidated. Here we report two cryo-EM structures of RuvB, providing a comprehensive understanding of HJ branch migration. RuvB assembles into a spiral staircase, ring-like hexamer, encircling dsDNA. Four protomers of RuvB contact the DNA backbone with a translocation step size of 2 nucleotides. The variation of nucleotide-binding states in RuvB supports a sequential model for ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide recycling, which occur at separate, singular positions. RuvB's asymmetric assembly also explains the 6:4 stoichiometry between the RuvB/RuvA complex, which coordinates HJ migration in bacteria. Taken together, we provide a mechanistic understanding of HJ branch migration facilitated by RuvB, which may be universally shared by prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Ohio State Biochemistry Program, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 43210, USA.