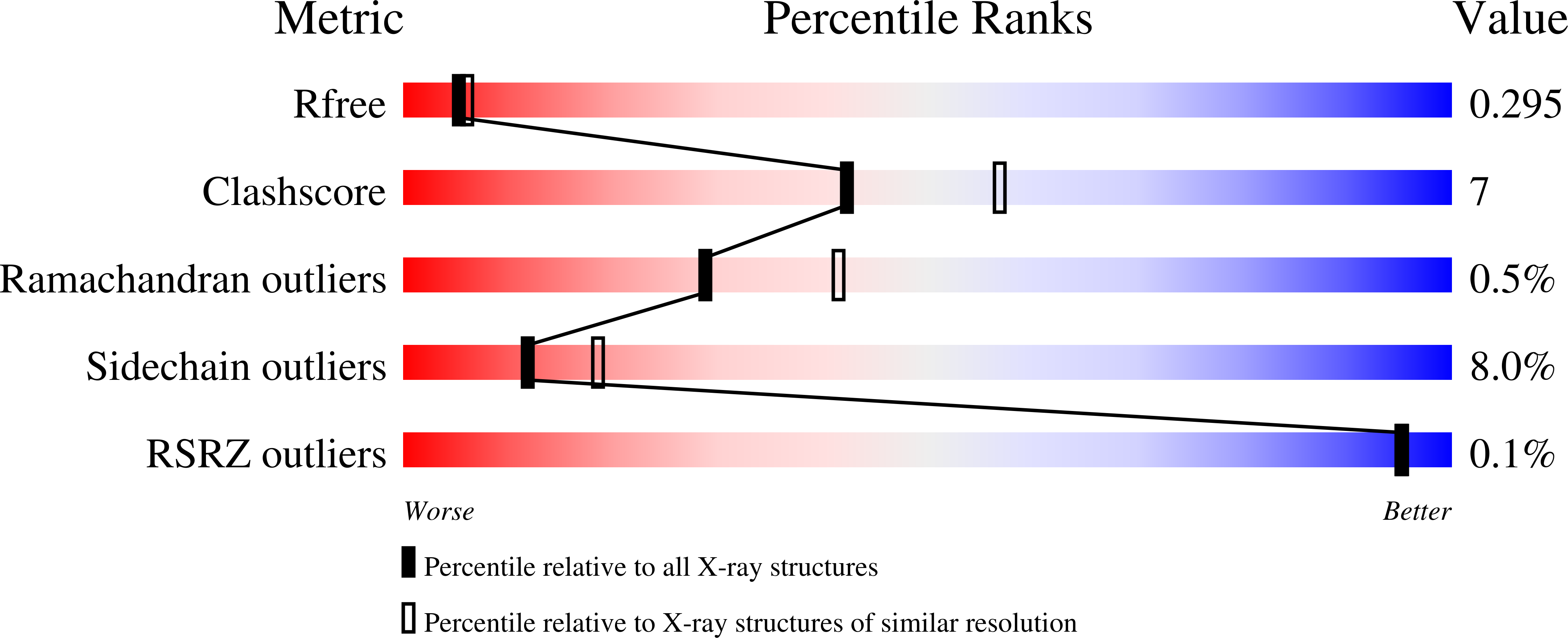
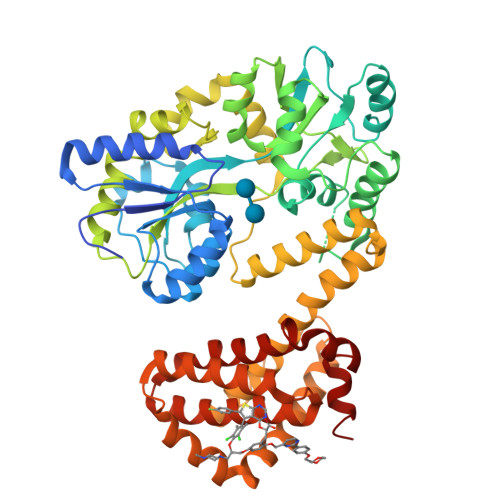
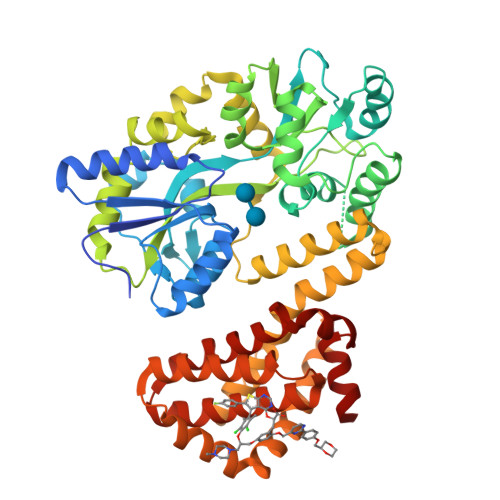
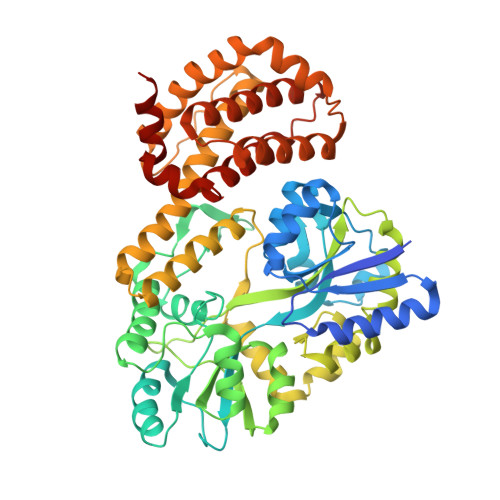
Selective MCL-1 inhibitor ABBV-467 is efficacious in tumor models but is associated with cardiac troponin increases in patients.
Yuda, J., Will, C., Phillips, D.C., Abraham, L., Alvey, C., Avigdor, A., Buck, W., Besenhofer, L., Boghaert, E., Cheng, D., Cojocari, D., Doyle, K., Hansen, T.M., Huang, K., Johnson, E.F., Judd, A.S., Judge, R.A., Kalvass, J.C., Kunzer, A., Lam, L.T., Li, R., Martin, R.L., Mastracchio, A., Mitten, M., Petrich, A., Wang, J., Ward, J.E., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Wolff, J.E., Bell-McGuinn, K.M., Souers, A.J.(2023) Commun Med (Lond) 3: 154-154
- PubMed: 37880389
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43856-023-00380-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EKX, 8EL0, 8EL1 - PubMed Abstract:
MCL-1 is a prosurvival B-cell lymphoma 2 family protein that plays a critical role in tumor maintenance and survival and can act as a resistance factor to multiple anticancer therapies. Herein, we describe the generation and characterization of the highly potent and selective MCL-1 inhibitor ABBV-467 and present findings from a first-in-human trial that included patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (NCT04178902). Binding of ABBV-467 to human MCL-1 was assessed in multiple cell lines. The ability of ABBV-467 to induce tumor growth inhibition was investigated in xenograft models of human multiple myeloma and acute myelogenous leukemia. The first-in-human study was a multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study assessing safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of ABBV-467 monotherapy. Here we show that administration of ABBV-467 to MCL-1-dependent tumor cell lines triggers rapid and mechanism-based apoptosis. In vivo, intermittent dosing of ABBV-467 as monotherapy or in combination with venetoclax inhibits the growth of xenografts from human hematologic cancers. Results from a clinical trial evaluating ABBV-467 in patients with multiple myeloma based on these preclinical data indicate that treatment with ABBV-467 can result in disease control (seen in 1 patient), but may also cause increases in cardiac troponin levels in the plasma in some patients (seen in 4 of 8 patients), without other corresponding cardiac findings. The selectivity of ABBV-467 suggests that treatment-induced troponin release is a consequence of MCL-1 inhibition and therefore may represent a class effect of MCL-1 inhibitors in human patients.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Cancer Center Hospital East, Kashiwa, Japan.