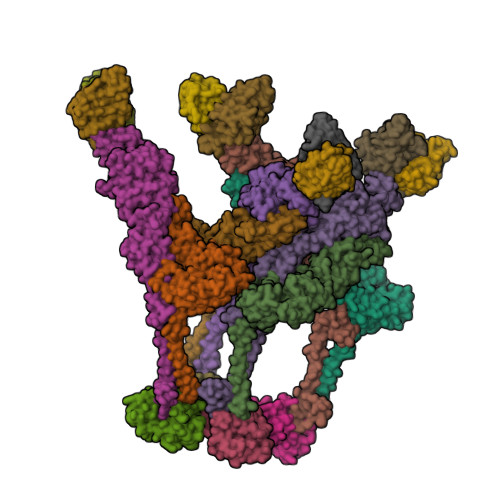
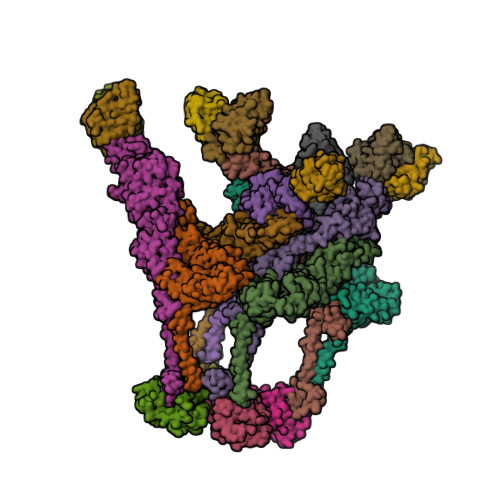
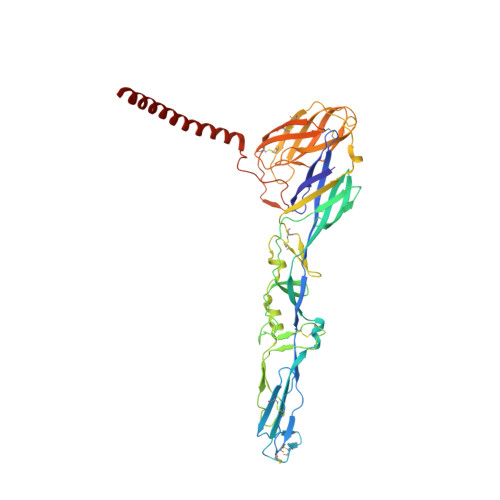
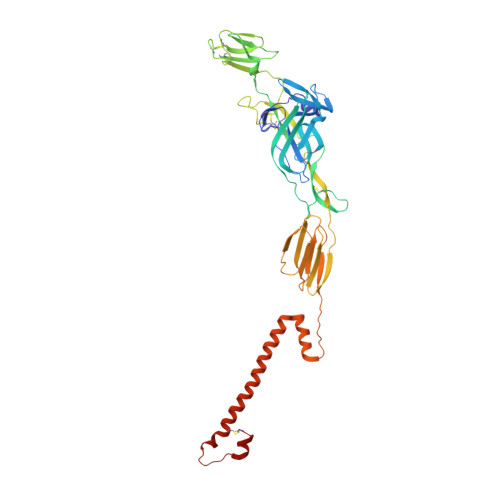
A chikungunya virus-like particle vaccine induces broadly neutralizing and protective antibodies against alphaviruses in humans.
Raju, S., Adams, L.J., Earnest, J.T., Warfield, K., Vang, L., Crowe Jr., J.E., Fremont, D.H., Diamond, M.S.(2023) Sci Transl Med 15: eade8273-eade8273
- PubMed: 37196061
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.ade8273
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DWW, 8DWX, 8DWY - PubMed Abstract:
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a mosquito-transmitted alphavirus that causes epidemics of acute and chronic musculoskeletal disease. Here, we analyzed the human B cell response to a CHIKV-like particle-adjuvanted vaccine (PXVX0317) from samples obtained from a phase 2 clinical trial in humans (NCT03483961). Immunization with PXVX0317 induced high levels of neutralizing antibody in serum against CHIKV and circulating antigen-specific B cells up to 6 months after immunization. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated from peripheral blood B cells of three PXVX0317-vaccinated individuals on day 57 after immunization potently neutralized CHIKV infection, and a subset of these inhibited multiple related arthritogenic alphaviruses. Epitope mapping and cryo-electron microscopy defined two broadly neutralizing mAbs that uniquely bind to the apex of the B domain of the E2 glycoprotein. These results demonstrate the inhibitory breadth and activity of the human B cell response induced by the PXVX0317 vaccine against CHIKV and potentially other related alphaviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO 63110, USA.