Potent and biostable inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2.
Tsuji, K., Ishii, T., Kobayakawa, T., Higashi-Kuwata, N., Azuma, C., Nakayama, M., Onishi, T., Nakano, H., Wada, N., Hori, M., Shinohara, K., Miura, Y., Kawada, T., Hayashi, H., Hattori, S.I., Bulut, H., Das, D., Takamune, N., Kishimoto, N., Saruwatari, J., Okamura, T., Nakano, K., Misumi, S., Mitsuya, H., Tamamura, H.(2022) iScience 25: 105365-105365
- PubMed: 36338434
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105365
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
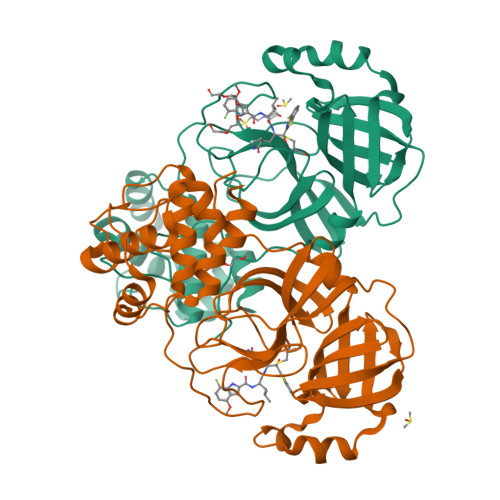
8DOY - PubMed Abstract:
Potent and biostable inhibitors of the main protease (M pro ) of SARS-CoV-2 were designed and synthesized based on an active hit compound 5h ( 2 ). Our strategy was based not only on the introduction of fluorine atoms into the inhibitor molecule for an increase of binding affinity for the pocket of M pro and cell membrane permeability but also on the replacement of the digestible amide bond by a surrogate structure to increase the biostability of the compounds. Compound 3 is highly potent and blocks SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro without a viral breakthrough. The derivatives, which contain a thioamide surrogate in the P2-P1 amide bond of these compounds ( 2 and 3 ), showed remarkably preferable pharmacokinetics in mice compared with the corresponding parent compounds. These data show that compounds 3 and its biostable derivative 4 are potential drugs for treating COVID-19 and that replacement of the digestible amide bond by its thioamide surrogate structure is an effective method.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Institute of Biomaterials and Bioengineering, Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU), Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0062, Japan.