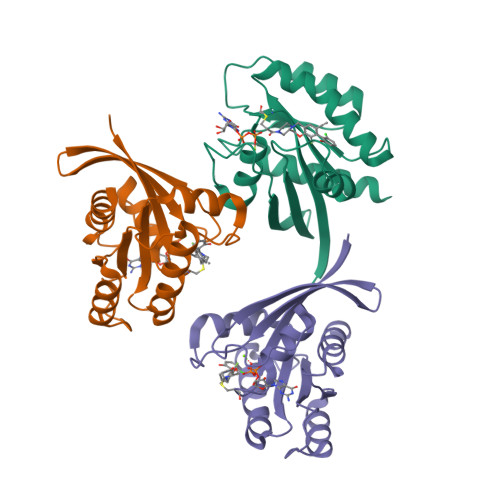
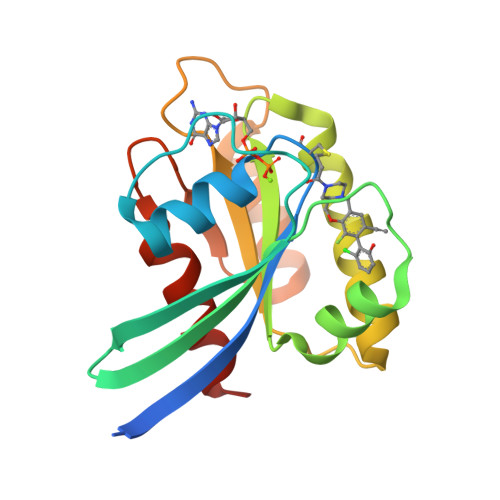
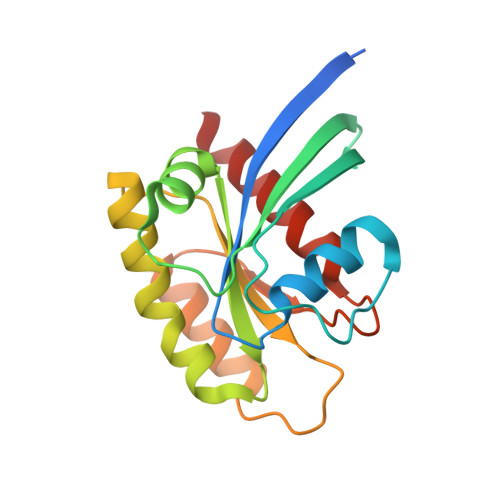
Modeling receptor flexibility in the structure-based design of KRAS G12C inhibitors.
Zhu, K., Li, C., Wu, K.Y., Mohr, C., Li, X., Lanman, B.(2022) J Comput Aided Mol Des 36: 591-604
- PubMed: 35930206
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-022-00467-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DNI, 8DNJ, 8DNK - PubMed Abstract:
KRAS has long been referred to as an 'undruggable' target due to its high affinity for its cognate ligands (GDP and GTP) and its lack of readily exploited allosteric binding pockets. Recent progress in the development of covalent inhibitors of KRAS G12C has revealed that occupancy of an allosteric binding site located between the α3-helix and switch-II loop of KRAS G12C -sometimes referred to as the 'switch-II pocket'-holds great potential in the design of direct inhibitors of KRAS G12C . In studying diverse switch-II pocket binders during the development of sotorasib (AMG 510), the first FDA-approved inhibitor of KRAS G12C , we found the dramatic conformational flexibility of the switch-II pocket posing significant challenges toward the structure-based design of inhibitors. Here, we present our computational approaches for dealing with receptor flexibility in the prediction of ligand binding pose and binding affinity. For binding pose prediction, we modified the covalent docking program CovDock to allow for protein conformational mobility. This new docking approach, termed as FlexCovDock, improves success rates from 55 to 89% for binding pose prediction on a dataset of 10 cross-docking cases and has been prospectively validated across diverse ligand chemotypes. For binding affinity prediction, we found standard free energy perturbation (FEP) methods could not adequately handle the significant conformational change of the switch-II loop. We developed a new computational strategy to accelerate conformational transitions through the use of targeted protein mutations. Using this methodology, the mean unsigned error (MUE) of binding affinity prediction were reduced from 1.44 to 0.89 kcal/mol on a set of 14 compounds. These approaches were of significant use in facilitating the structure-based design of KRAS G12C inhibitors and are anticipated to be of further use in the design of covalent (and noncovalent) inhibitors of other conformationally labile protein targets.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Engineering, Amgen Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA, 91320, USA. kzhu@amgen.com.