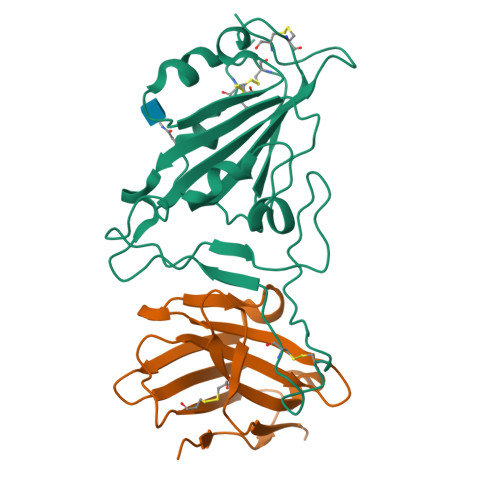
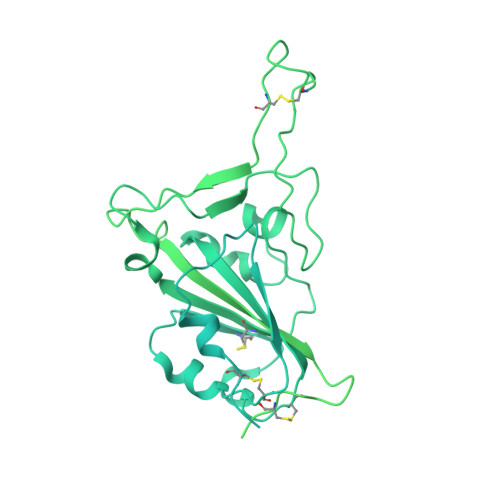
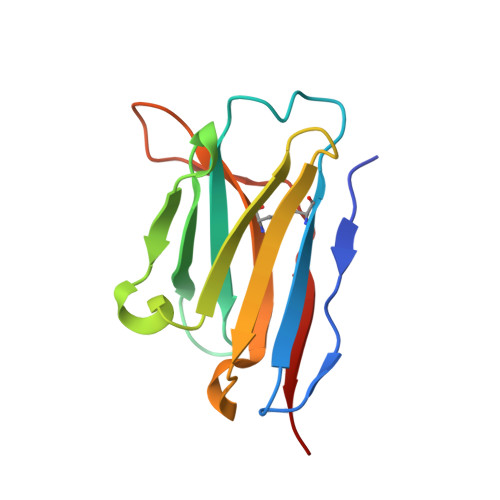
Potent and broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) including omicron sub-lineages BA.1 and BA.2 by biparatopic human VH domains.
Chen, C., Saville, J.W., Marti, M.M., Schafer, A., Cheng, M.H., Mannar, D., Zhu, X., Berezuk, A.M., Banerjee, A., Sobolewski, M.D., Kim, A., Treat, B.R., Da Silva Castanha, P.M., Enick, N., McCormick, K.D., Liu, X., Adams, C., Hines, M.G., Sun, Z., Chen, W., Jacobs, J.L., Barratt-Boyes, S.M., Mellors, J.W., Baric, R.S., Bahar, I., Dimitrov, D.S., Subramaniam, S., Martinez, D.R., Li, W.(2022) iScience 25: 104798-104798
- PubMed: 35875685
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.104798
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DI5 - PubMed Abstract:
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) requires the development of next-generation biologics with high neutralization breadth. Here, we characterized a human V H domain, F6, which we generated by sequentially panning large phage-displayed V H libraries against receptor binding domains (RBDs) containing VOC mutations. Cryo-EM analyses reveal that F6 has a unique binding mode that spans a broad surface of the RBD and involves the antibody framework region. Attachment of an Fc region to a fusion of F6 and ab8, a previously characterized V H domain, resulted in a construct (F6-ab8-Fc) that broadly and potently neutralized VOCs including Omicron. Additionally, prophylactic treatment using F6-ab8-Fc reduced live Beta (B.1.351) variant viral titers in the lungs of a mouse model. Our results provide a new potential therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron and highlight a vulnerable epitope within the spike that may be exploited to achieve broad protection against circulating variants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Antibody Therapeutics, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh Medical School, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.