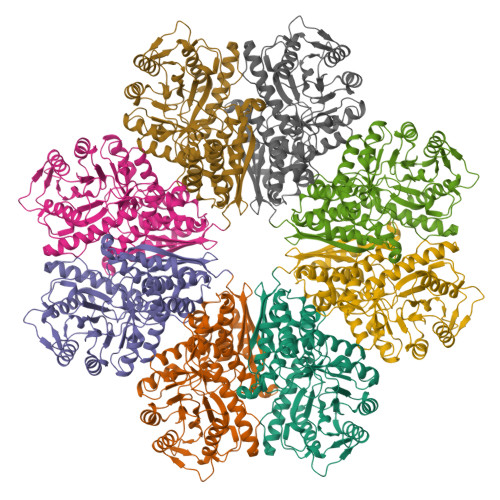
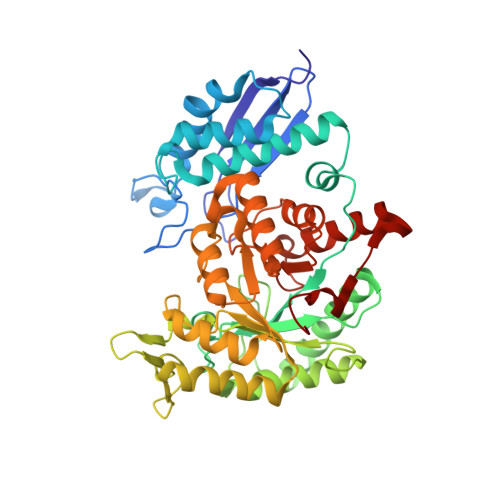
High-Resolution Single-Particle Cryo-EM Hydrated Structure of Streptococcus pyogenes Enolase Offers Insights into Its Function as a Plasminogen Receptor.
Tjia-Fleck, S., Readnour, B.M., Ayinuola, Y.A., Castellino, F.J.(2023) Biochemistry 62: 735-746
- PubMed: 36701429
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00637
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7UGU, 8DG4 - PubMed Abstract:
Cellular plasminogen (Pg) receptors (PgRs) are utilized to recruit Pg; stimulate its activation to the serine protease, plasmin (Pm); and sterically protect the surface Pm from inactivation by host inhibitors. One such PgR is the moonlighting enzyme, enolase, some of which leaves the cytoplasm and resides at the cell surface to potentially function as a PgR. Since microbes employ conscription of host Pg by PgRs as one virulence mechanism, we explored the structural basis of the ability of Streptococcus pyogenes enolase (Sen) to function in this manner. Employing single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), recombinant Sen from S. pyogenes was modeled at 2.6 Å as a stable symmetrical doughnut-shaped homooctamer with point group 422 (D4) symmetry, with a monomeric subunit molecular weight of ∼49 kDa. Binding sites for hPg were reported in other studies to include an internal K 252,255 and the COOH-terminal K 434,435 residues of Sen. However, in native Sen, the latter are buried within the minor interfaces of the octamer and do not function as a Pg-binding epitope. Whereas Sen and hPg do not interact in solution, when Sen is bound to a surface, hPg interacts with Sen independently of K 252,255,434,435 . PgRs devoid of COOH-terminal lysine utilize lysine isosteres comprising a basic residue, " i ", and an anionic residue at " i + 3" around one turn of an α-helix. We highlight a number of surface-exposed potential hPg-binding lysine isosteres and further conclude that while the octameric structure of Sen is critical for hPg binding, disruption of this octamer without dissociation exposes hPg-binding epitopes.
Organizational Affiliation:
W.M. Keck Center for Transgene Research, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556, United States.