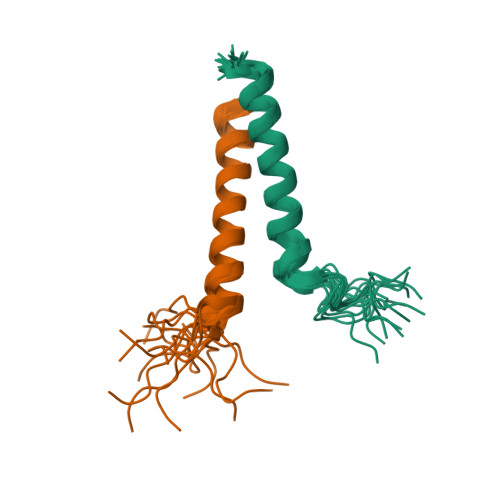
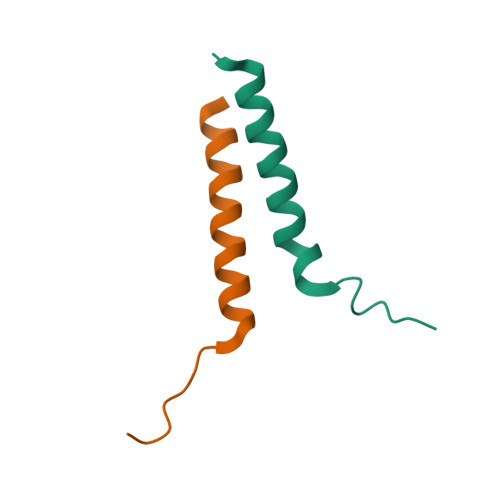
Structural basis of gamma chain family receptor sharing at the membrane level.
Cai, T., Lenoir Capello, R., Pi, X., Wu, H., Chou, J.J.(2023) Science 381: 569-576
- PubMed: 37535730
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.add1219
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DDC, 8DDD - PubMed Abstract:
Common γ chain (γc) cytokine receptors, including interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21 receptors, are activated upon engagement with a common γc receptor (CD132) by concomitant binding of their ectodomains to an interleukin. In this work, we find that direct interactions between the transmembrane domains (TMDs) of both the γc and the interleukin receptors (ILRs) are also required for receptor activation. Moreover, the same γc TMD can specifically recognize multiple ILR TMDs of diverse sequences within the family. Heterodimer structures of γc TMD bound to IL-7 and IL-9 receptor TMDs-determined in a lipid bilayer-like environment by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-reveal a conserved knob-into-hole mechanism of recognition that mediates receptor sharing within the membrane. Thus, signaling in the γc receptor family requires specific heterotypic interactions of the TMDs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.