Broadly neutralizing antibodies target the coronavirus fusion peptide.
Dacon, C., Tucker, C., Peng, L., Lee, C.D., Lin, T.H., Yuan, M., Cong, Y., Wang, L., Purser, L., Williams, J.K., Pyo, C.W., Kosik, I., Hu, Z., Zhao, M., Mohan, D., Cooper, A.J.R., Peterson, M., Skinner, J., Dixit, S., Kollins, E., Huzella, L., Perry, D., Byrum, R., Lembirik, S., Drawbaugh, D., Eaton, B., Zhang, Y., Yang, E.S., Chen, M., Leung, K., Weinberg, R.S., Pegu, A., Geraghty, D.E., Davidson, E., Douagi, I., Moir, S., Yewdell, J.W., Schmaljohn, C., Crompton, P.D., Holbrook, M.R., Nemazee, D., Mascola, J.R., Wilson, I.A., Tan, J.(2022) Science 377: 728-735
- PubMed: 35857439
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abq3773
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
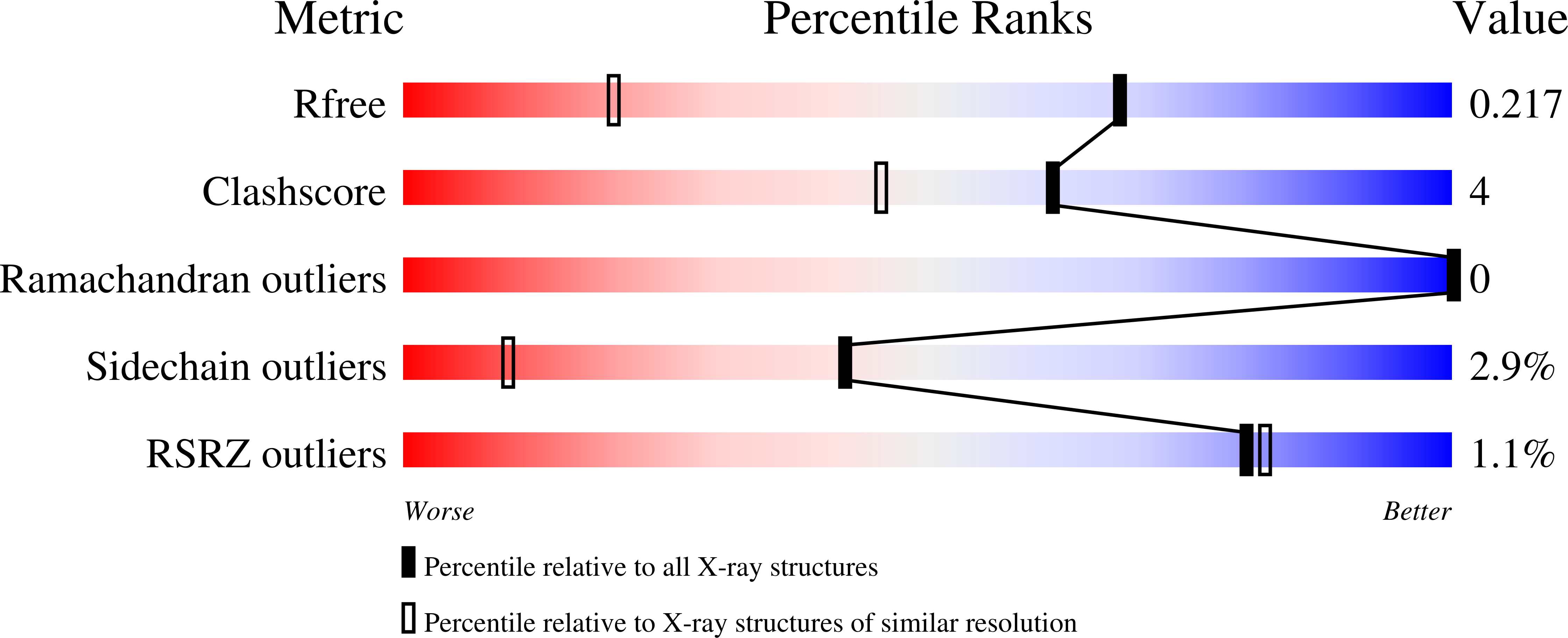
8D36, 8D6Z, 8DAO - PubMed Abstract:
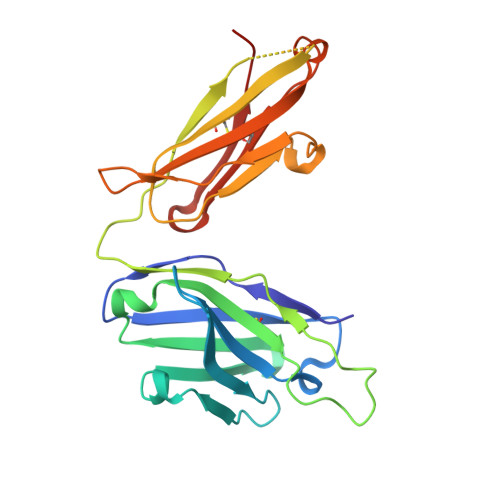
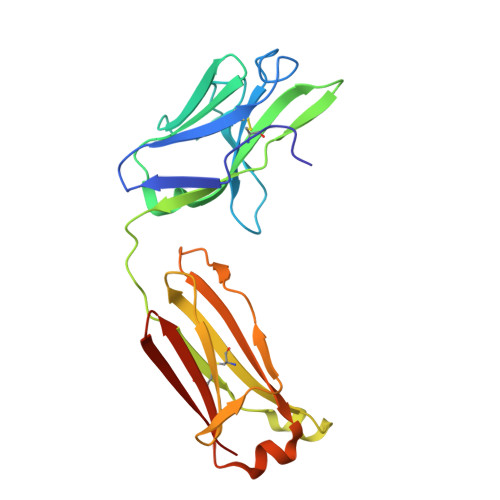
The potential for future coronavirus outbreaks highlights the need to broadly target this group of pathogens. We used an epitope-agnostic approach to identify six monoclonal antibodies that bind to spike proteins from all seven human-infecting coronaviruses. All six antibodies target the conserved fusion peptide region adjacent to the S2' cleavage site. COV44-62 and COV44-79 broadly neutralize alpha- and betacoronaviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron subvariants BA.2 and BA.4/5, albeit with lower potency than receptor binding domain-specific antibodies. In crystal structures of COV44-62 and COV44-79 antigen-binding fragments with the SARS-CoV-2 fusion peptide, the fusion peptide epitope adopts a helical structure and includes the arginine residue at the S2' cleavage site. COV44-79 limited disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 in a Syrian hamster model. These findings highlight the fusion peptide as a candidate epitope for next-generation coronavirus vaccine development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Antibody Biology Unit, Laboratory of Immunogenetics, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD 20852, USA.