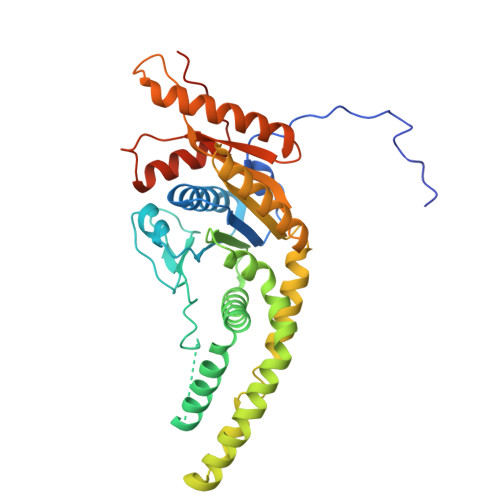
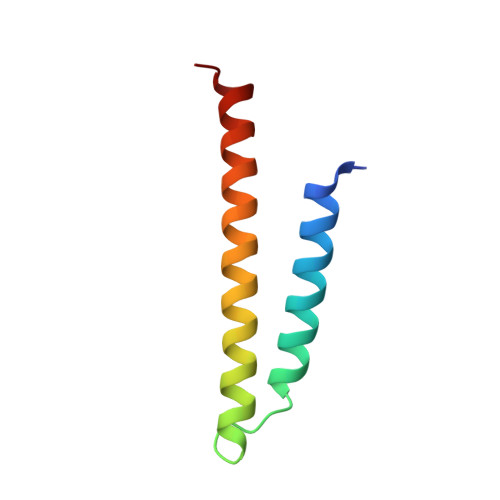
The GET insertase exhibits conformational plasticity and induces membrane thinning.
McDowell, M.A., Heimes, M., Enkavi, G., Farkas, A., Saar, D., Wild, K., Schwappach, B., Vattulainen, I., Sinning, I.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 7355-7355
- PubMed: 37963916
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42867-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CQZ, 8CR1, 8CR2, 8ODU, 8ODV - PubMed Abstract:
The eukaryotic guided entry of tail-anchored proteins (GET) pathway mediates the biogenesis of tail-anchored (TA) membrane proteins at the endoplasmic reticulum. In the cytosol, the Get3 chaperone captures the TA protein substrate and delivers it to the Get1/Get2 membrane protein complex (GET insertase), which then inserts the substrate via a membrane-embedded hydrophilic groove. Here, we present structures, atomistic simulations and functional data of human and Chaetomium thermophilum Get1/Get2/Get3. The core fold of the GET insertase is conserved throughout eukaryotes, whilst thinning of the lipid bilayer occurs in the vicinity of the hydrophilic groove to presumably lower the energetic barrier of membrane insertion. We show that the gating interaction between Get2 helix α3' and Get3 drives conformational changes in both Get3 and the Get1/Get2 membrane heterotetramer. Thus, we provide a framework to understand the conformational plasticity of the GET insertase and how it remodels its membrane environment to promote substrate insertion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center (BZH), Im Neuenheimer Feld 328, 69120, Heidelberg, Germany. melanie.mcdowell@biophys.mpg.de.