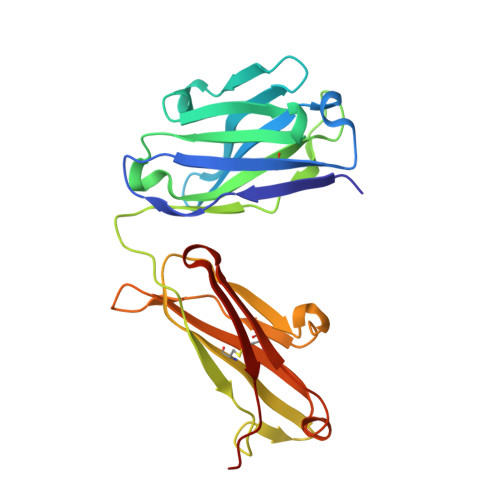
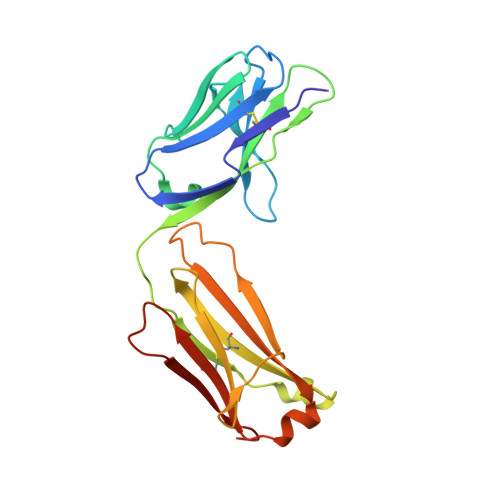
Serum albumin binding knob domains engineered within a V H framework III bispecific antibody format and as chimeric peptides.
Adams, R., Joyce, C., Kuravskiy, M., Harrison, K., Ahdash, Z., Balmforth, M., Chia, K., Marceddu, C., Coates, M., Snowden, J., Goursaud, E., Menochet, K., van den Elsen, J., Payne, R.J., Lawson, A.D.G., Scott-Tucker, A., Macpherson, A.(2023) Front Immunol 14: 1170357-1170357
- PubMed: 37251411
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1170357
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8C7J, 8C7V - PubMed Abstract:
Serum albumin binding is an established mechanism to extend the serum half-life of antibody fragments and peptides. The cysteine rich knob domains, isolated from bovine antibody ultralong CDRH3, are the smallest single chain antibody fragments described to date and versatile tools for protein engineering. Here, we used phage display of bovine immune material to derive knob domains against human and rodent serum albumins. These were used to engineer bispecific Fab fragments, by using the framework III loop as a site for knob domain insertion. By this route, neutralisation of the canonical antigen (TNFα) was retained but extended pharmacokinetics in-vivo were achieved through albumin binding. Structural characterisation revealed correct folding of the knob domain and identified broadly common but non-cross-reactive epitopes. Additionally, we show that these albumin binding knob domains can be chemically synthesised to achieve dual IL-17A neutralisation and albumin binding in a single chemical entity. This study enables antibody and chemical engineering from bovine immune material, via an accessible discovery platform.
Organizational Affiliation:
Early Solutions, UCB Biopharma UK, Slough, United Kingdom.