Structural basis for ubiquitylation by HOIL-1.
Wu, Q., Koliopoulos, M.G., Rittinger, K., Stieglitz, B.(2022) Front Mol Biosci 9: 1098144-1098144
- PubMed: 36685275
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.1098144
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BVL - PubMed Abstract:
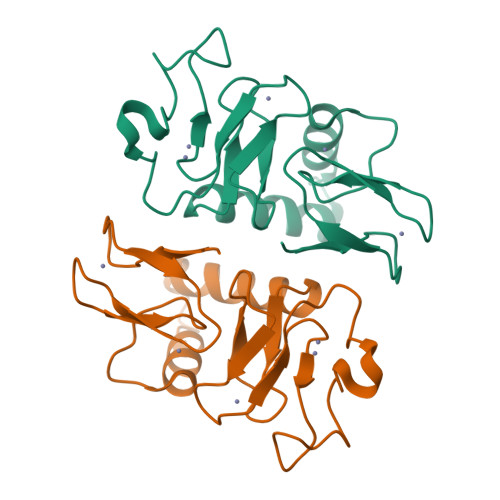
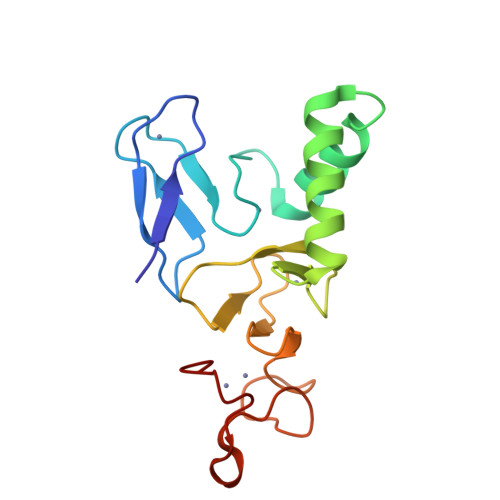
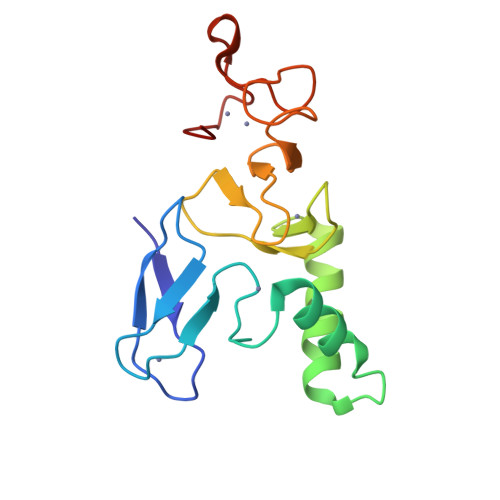
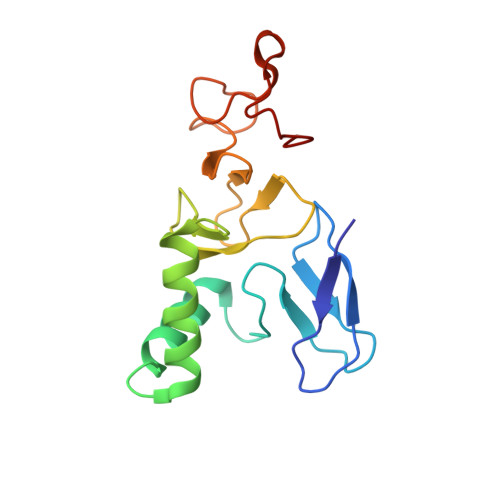
The linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex synthesises linear Ub chains which constitute a binding and activation platform for components of the TNF signalling pathway. One of the components of LUBAC is the ubiquitin ligase HOIL-1 which has been shown to generate oxyester linkages on several proteins and on linear polysaccharides. We show that HOIL-1 activity requires linear tetra-Ub binding which enables HOIL-1 to mono-ubiquitylate linear Ub chains and polysaccharides. Furthermore, we describe the crystal structure of a C-terminal tandem domain construct of HOIL-1 comprising the IBR and RING2 domains. Interestingly, the structure reveals a unique bi-nuclear Zn-cluster which substitutes the second zinc finger of the canonical RING2 fold. We identify the C-terminal histidine of this bi-nuclear Zn-cluster as the catalytic base required for the ubiquitylation activity of HOIL-1. Our study suggests that the unique zinc-coordinating architecture of RING2 provides a binding platform for ubiquitylation targets.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, School of Biological and Behavioural Sciences, Queen Mary University of London, London, United Kingdom.