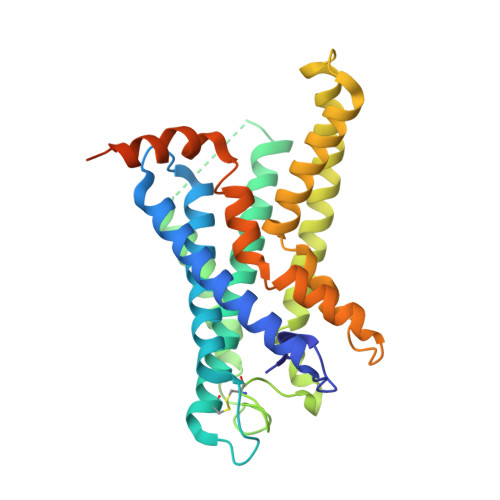
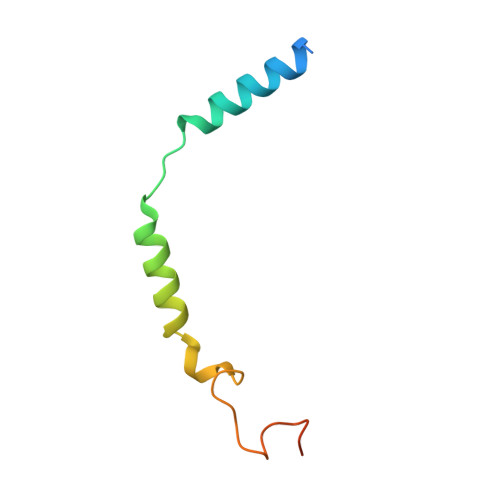
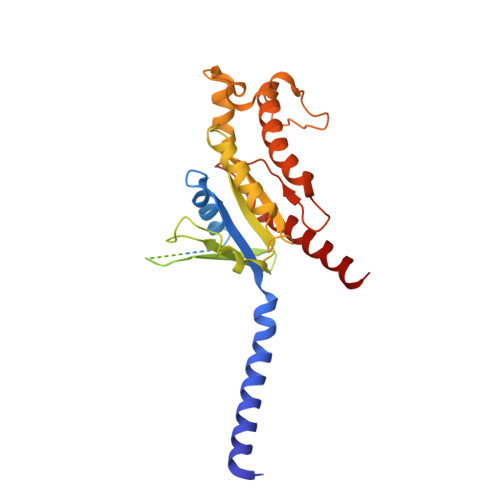
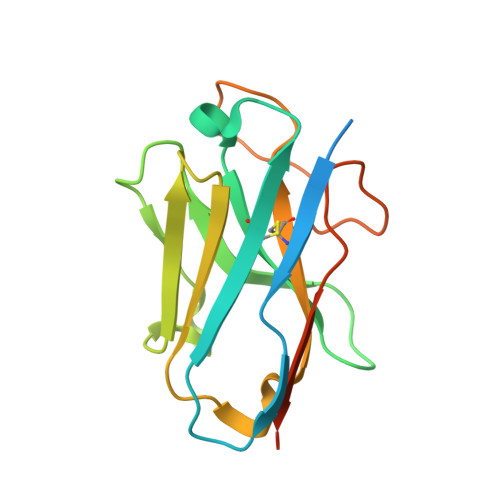
Structural basis of CD97 activation and G-protein coupling.
Wang, N., Qian, Y., Xia, R., Zhu, X., Xiong, Y., Zhang, A., Guo, C., He, Y.(2023) Cell Chem Biol 30: 1343-1353.e5
- PubMed: 37673067
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.08.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YDH, 7YDM, 7YDP - PubMed Abstract:
CD97 (ADGRE5) is an adhesion G protein-coupled receptor (aGPCR) which plays crucial roles in immune system and cancer. However, the mechanism of CD97 activation and the determinant of G 13 coupling selectivity remain unknown. Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of human CD97 in complex with G 13 , G q , and G s . Our structures reveal the stalk peptide recognition mode of CD97, adding missing information of the current tethered-peptide activation model of aGPCRs. For instance, a revised "FXφφφ" motif and a framework of conserved aromatic residues in the ligand-binding pocket. Importantly, structural comparisons of G 13 , G q , and G s engagements of CD97 reveal key determinants of G 13 coupling selectivity, where a deep insertion of the α helix 5 and a closer contact with the transmembrane helix 6, 5, and 3 dictate coupling preferences. Taken together, our structural study of CD97 provides a framework for understanding CD97 signaling and the G 13 coupling selectivity.
- Laboratory of Receptor Structure and Signaling, HIT Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China.
Organizational Affiliation: