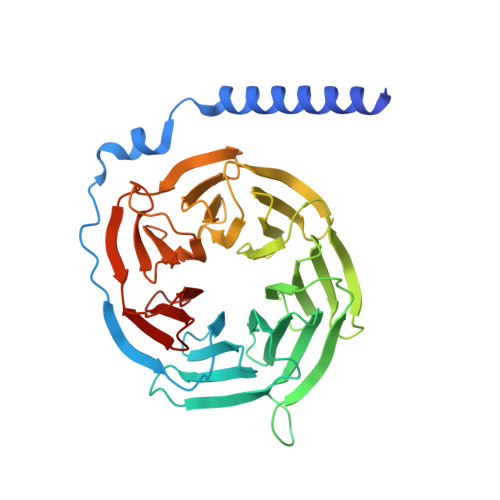
Activation and signaling mechanism revealed by GPR119-G s complex structures.
Qian, Y., Wang, J., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Liu, W., Lin, Y., Yang, H., Ma, L., Ye, S., Wu, S., Qiao, A.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 7033-7033
- PubMed: 36396650
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34696-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WCM, 7WCN - PubMed Abstract:
Agonists selectively targeting cannabinoid receptor-like G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR119 hold promise for treating metabolic disorders while avoiding unwanted side effects. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the human GPR119-G s signaling complexes bound to AR231453 and MBX-2982, two representative agonists reported for GPR119. The structures reveal a one-amino acid shift of the conserved proline residue of TM5 that forms an outward bulge, opening up a hydrophobic cavity between TM4 and TM5 at the middle of the membrane for its endogenous ligands-monounsaturated lipid metabolites. In addition, we observed a salt bridge between ICL1 of GPR119 and Gβ s . Disruption of the salt bridge eliminates the cAMP production of GPR119, indicating an important role of Gβ s in GPR119-mediated signaling. Our structures, together with mutagenesis studies, illustrate the conserved binding mode of the chemically different agonists, and provide insights into the conformational changes in receptor activation and G protein coupling.
- Frontiers Science Center for Synthetic Biology (Ministry of Education), Tianjin Key Laboratory of Function and Application of Biological Macromolecular Structures, School of Life Sciences, Tianjin University, Tianjin, P. R. China.
Organizational Affiliation: