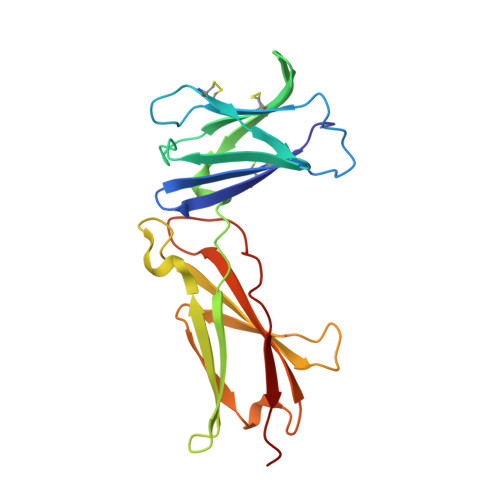
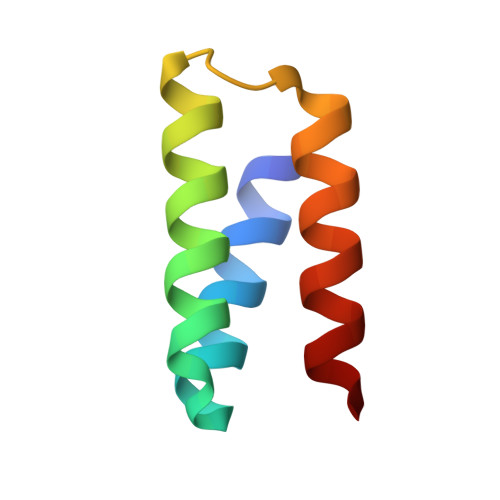
Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone.
Cao, L., Coventry, B., Goreshnik, I., Huang, B., Sheffler, W., Park, J.S., Jude, K.M., Markovic, I., Kadam, R.U., Verschueren, K.H.G., Verstraete, K., Walsh, S.T.R., Bennett, N., Phal, A., Yang, A., Kozodoy, L., DeWitt, M., Picton, L., Miller, L., Strauch, E.M., DeBouver, N.D., Pires, A., Bera, A.K., Halabiya, S., Hammerson, B., Yang, W., Bernard, S., Stewart, L., Wilson, I.A., Ruohola-Baker, H., Schlessinger, J., Lee, S., Savvides, S.N., Garcia, K.C., Baker, D.(2022) Nature 605: 551-560
- PubMed: 35332283
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04654-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7N1J, 7N1K, 7N3T, 7OPB, 7RDH, 7S5B - PubMed Abstract:
The design of proteins that bind to a specific site on the surface of a target protein using no information other than the three-dimensional structure of the target remains a challenge 1-5 . Here we describe a general solution to this problem that starts with a broad exploration of the vast space of possible binding modes to a selected region of a protein surface, and then intensifies the search in the vicinity of the most promising binding modes. We demonstrate the broad applicability of this approach through the de novo design of binding proteins to 12 diverse protein targets with different shapes and surface properties. Biophysical characterization shows that the binders, which are all smaller than 65 amino acids, are hyperstable and, following experimental optimization, bind their targets with nanomolar to picomolar affinities. We succeeded in solving crystal structures of five of the binder-target complexes, and all five closely match the corresponding computational design models. Experimental data on nearly half a million computational designs and hundreds of thousands of point mutants provide detailed feedback on the strengths and limitations of the method and of our current understanding of protein-protein interactions, and should guide improvements of both. Our approach enables the targeted design of binders to sites of interest on a wide variety of proteins for therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: