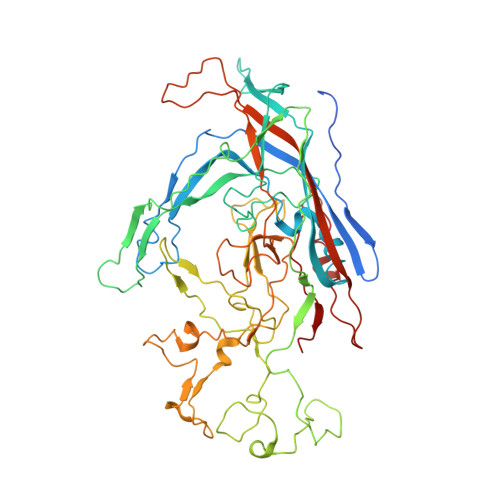
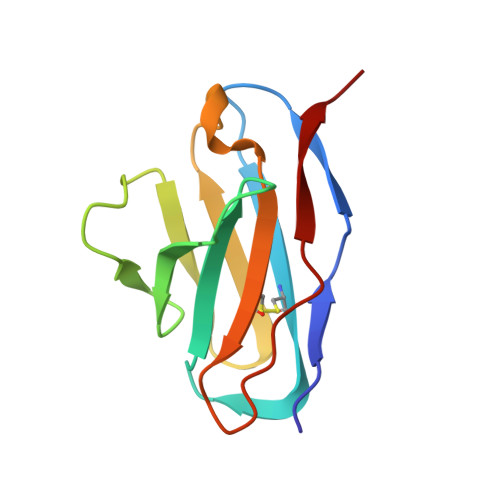
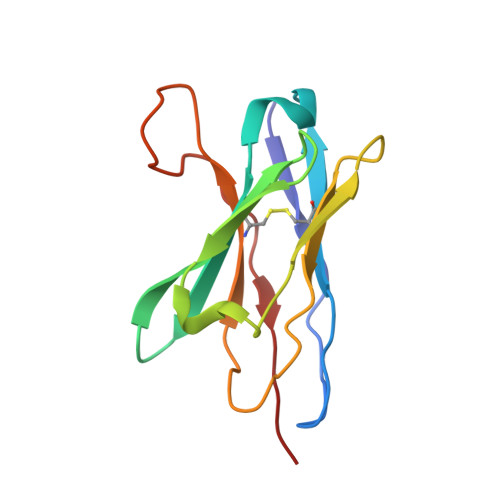
High-resolution asymmetric structure of a Fab-virus complex reveals overlap with the receptor binding site.
Goetschius, D.J., Hartmann, S.R., Organtini, L.J., Callaway, H., Huang, K., Bator, C.M., Ashley, R.E., Makhov, A.M., Conway, J.F., Parrish, C.R., Hafenstein, S.L.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 34074770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2025452118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7M3L, 7M3M, 7M3N, 7M3O - PubMed Abstract:
Canine parvovirus is an important pathogen causing severe diseases in dogs, including acute hemorrhagic enteritis, myocarditis, and cerebellar disease. Overlap on the surface of parvovirus capsids between the antigenic epitope and the receptor binding site has contributed to cross-species transmission, giving rise to closely related variants. It has been shown that Mab 14 strongly binds and neutralizes canine but not feline parvovirus, suggesting this antigenic site also controls species-specific receptor binding. To visualize the conformational epitope at high resolution, we solved the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the Fab-virus complex. We also created custom software, Icosahedral Subparticle Extraction and Correlated Classification, to solve a Fab-virus complex with only a few Fab bound per capsid and visualize local structures of the Fab-bound and -unbound antigenic sites extracted from the same complex map. Our results identified the antigenic epitope that had significant overlap with the receptor binding site, and the structures revealed that binding of Fab induced conformational changes to the virus. We were also able to assign the order and position of attached Fabs to allow assessment of complementarity between the Fabs bound to different positions. This approach therefore provides a method for using cryo-EM to investigate complementarity of antibody binding.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802.
Organizational Affiliation: