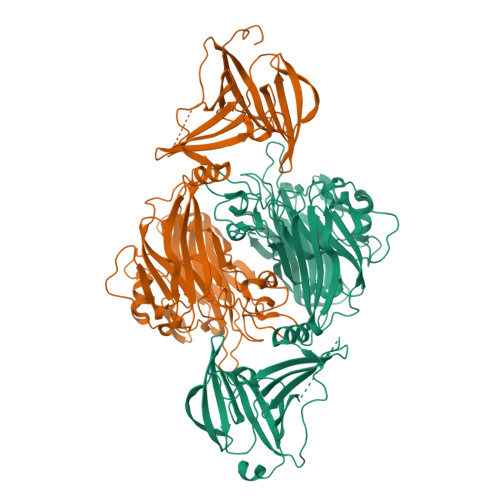
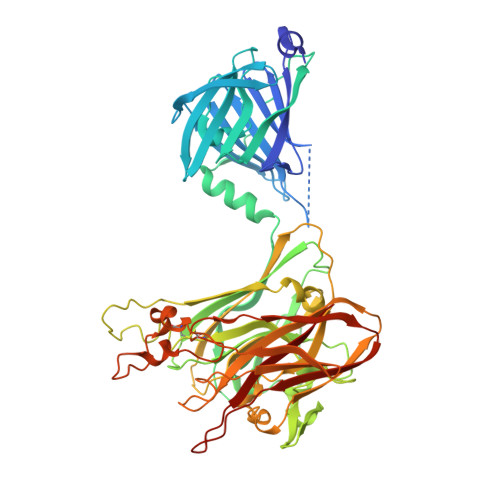
Plant N -glycan breakdown by human gut Bacteroides.
Crouch, L.I., Urbanowicz, P.A., Basle, A., Cai, Z.P., Liu, L., Voglmeir, J., Melo Diaz, J.M., Benedict, S.T., Spencer, D.I.R., Bolam, D.N.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2208168119-e2208168119
- PubMed: 36122227
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2208168119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ZGM, 7ZGN - PubMed Abstract:
The major nutrients available to the human colonic microbiota are complex glycans derived from the diet. To degrade this highly variable mix of sugar structures, gut microbes have acquired a huge array of different carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), predominantly glycoside hydrolases, many of which have specificities that can be exploited for a range of different applications. Plant N -glycans are prevalent on proteins produced by plants and thus components of the diet, but the breakdown of these complex molecules by the gut microbiota has not been explored. Plant N -glycans are also well characterized allergens in pollen and some plant-based foods, and when plants are used in heterologous protein production for medical applications, the N -glycans present can pose a risk to therapeutic function and stability. Here we use a novel genome association approach for enzyme discovery to identify a breakdown pathway for plant complex N -glycans encoded by a gut Bacteroides species and biochemically characterize five CAZymes involved, including structures of the PNGase and GH92 α-mannosidase. These enzymes provide a toolbox for the modification of plant N -glycans for a range of potential applications. Furthermore, the keystone PNGase also has activity against insect-type N -glycans, which we discuss from the perspective of insects as a nutrient source.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Microbiology and Infection, College of Medical and Dental Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, United Kingdom.