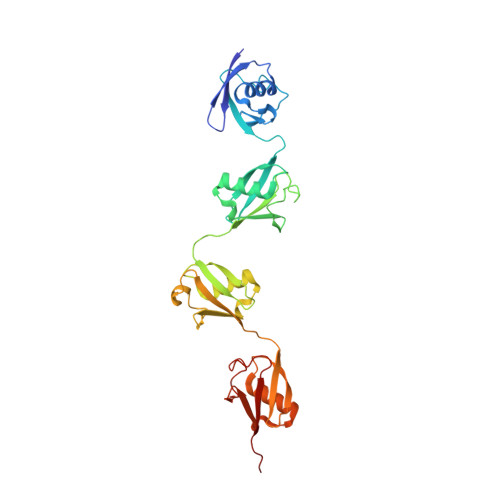
Mechanistic insights into the enzymatic activity of E3 ligase HOIL-1L and its regulation by the linear ubiquitin chain binding.
Xu, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Yin, Y., Peng, C., Gong, X., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Tang, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, H., Pan, L.(2023) Sci Adv 9: eadi4599-eadi4599
- PubMed: 37831767
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi4599
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YUI, 7YUJ - PubMed Abstract:
Heme-oxidized IRP2 ubiquitin ligase 1 (HOIL-1L) serves as a unique E3 ligase to catalyze the mono-ubiquitination of relevant protein or sugar substrates and plays vital roles in numerous cellular processes in mammals. However, the molecular mechanism underpinning the E3 activity of HOIL-1L and the related regulatory mechanism remain elusive. Here, we report the crystal structure of the catalytic core region of HOIL-1L and unveil the key catalytic triad residues of HOIL-1L. Moreover, we discover that HOIL-1L contains two distinct linear di-ubiquitin binding sites that can synergistically bind to linear tetra-ubiquitin, and the binding of HOIL-1L with linear tetra-ubiquitin can promote its E3 activity. The determined HOIL-1L/linear tetra-ubiquitin complex structure not only elucidates the detailed binding mechanism of HOIL-1L with linear tetra-ubiquitin but also uncovers a unique allosteric ubiquitin-binding site for the activation of HOIL-1L. In all, our findings provide mechanistic insights into the E3 activity of HOIL-1L and its regulation by the linear ubiquitin chain binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1 Sub-lane Xiangshan, Hangzhou 310024, China.