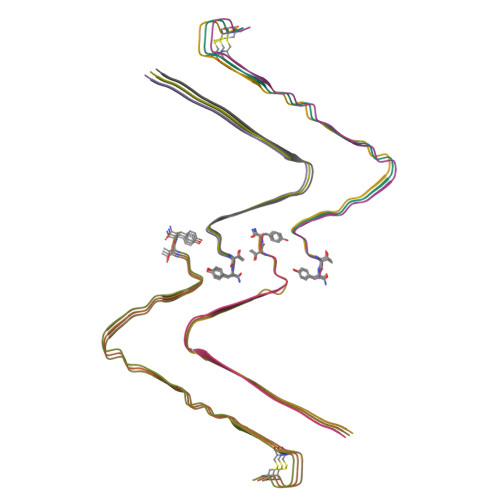
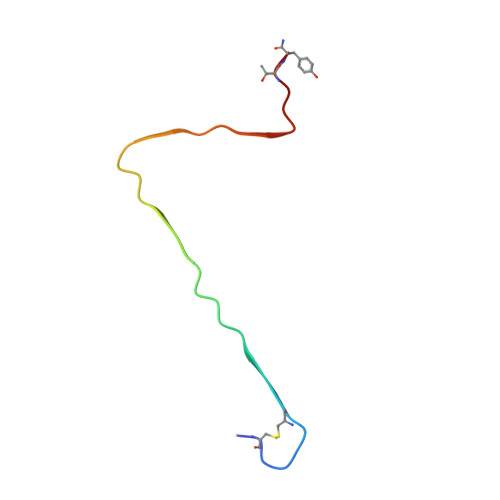
A new polymorphism of human amylin fibrils with similar protofilaments and a conserved core.
Li, D., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Song, K., Bao, K., Zhu, P.(2022) iScience 25: 105705-105705
- PubMed: 36567711
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105705
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YKW, 7YL0, 7YL3, 7YL7 - PubMed Abstract:
Pancreatic amyloid deposits composed of a fibrillar form of the human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) are the pathological hallmark of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Although various cryo-EM structures of polymorphic hIAPP fibrils were reported, the underlying polymorphic mechanism of hIAPP remains elusive. Meanwhile, the structure of hIAPP fibrils with all residues visible in the fibril core is not available. Here, we report the full-length structures of two different polymorphs of hIAPP fibrils, namely slim form (SF, dimer) and thick form (TF, tetramer), formed in a salt-free environment, which share a similar ζ-shaped protofilament but differ in inter-protofilament interfaces. In the absence of salt, electrostatic interactions were found to play a dominant role in stabilizing the fibril structure, suggesting an antagonistic effect between electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions in different salt concentrations environments. Our results shed light on understanding the mechanism of amyloid fibril polymorphism.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.