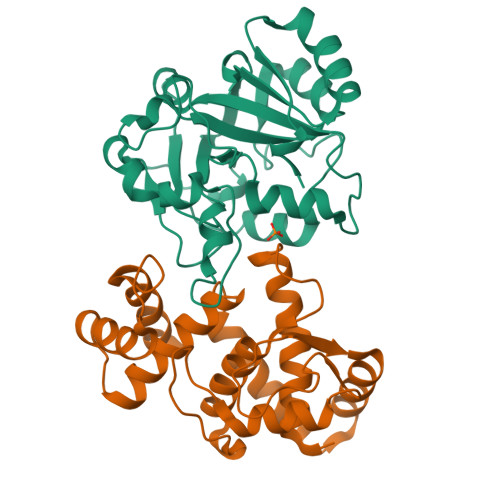
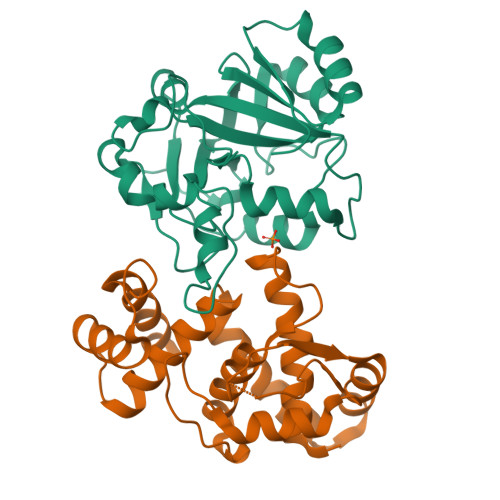
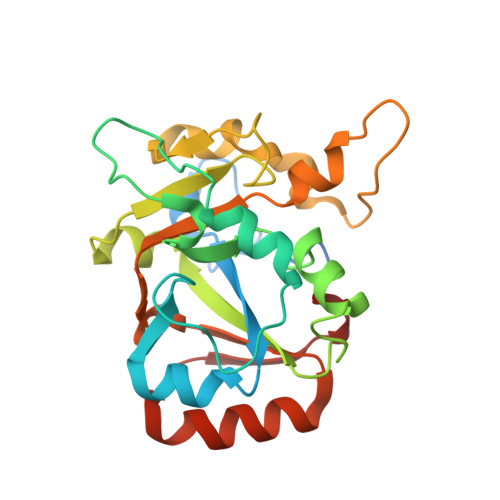
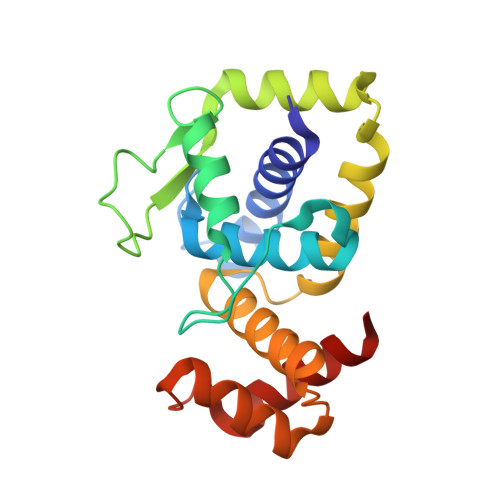
Structural insights into DarT toxin neutralization by cognate DarG antitoxin: ssDNA mimicry by DarG C-terminal domain keeps the DarT toxin inhibited.
Deep, A., Singh, L., Kaur, J., Velusamy, M., Bhardwaj, P., Singh, R., Thakur, K.G.(2023) Structure 31: 780-789.e4
- PubMed: 37167974
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2023.04.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YK3 - PubMed Abstract:
In the DarTG toxin-antitoxin system, the DarT toxin ADP-ribosylates single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), which stalls DNA replication and plays a crucial role in controlling bacterial growth and bacteriophage infection. This toxic activity is reversed by the N-terminal macrodomain of the cognate antitoxin DarG. DarG also binds DarT, but the role of these interactions in DarT neutralization is unknown. Here, we report that the C-terminal domain of DarG (DarG toxin-binding domain [DarG TBD ]) interacts with DarT to form a 1:1 stoichiometric heterodimeric complex. We determined the 2.2 Å resolution crystal structure of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis DarT-DarG TBD complex. The comparative structural analysis reveals that DarG TBD interacts with DarT at the DarT/ssDNA interaction interface, thus sterically occluding substrate ssDNA binding and consequently inactivating toxin by direct protein-protein interactions. Our data support a unique two-layered DarT toxin neutralization mechanism of DarG, which is important in keeping the toxin molecules in check under normal growth conditions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-Institute of Microbial Technology (CSIR-IMTECH), Chandigarh 160036, India.