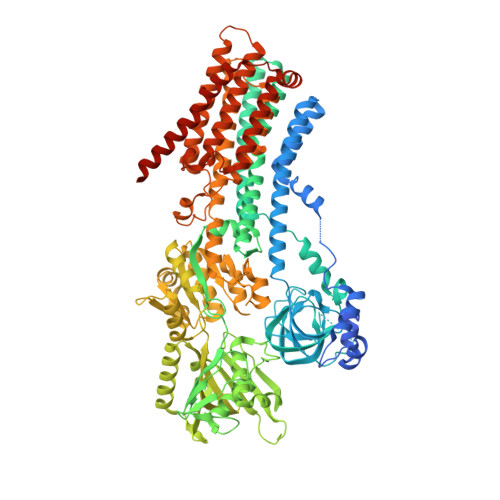
Cryo-EM structures of human SPCA1a reveal the mechanism of Ca 2+ /Mn 2+ transport into the Golgi apparatus.
Chen, Z., Watanabe, S., Hashida, H., Inoue, M., Daigaku, Y., Kikkawa, M., Inaba, K.(2023) Sci Adv 9: eadd9742-eadd9742
- PubMed: 36867705
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.add9742
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YAG, 7YAH, 7YAI, 7YAJ, 7YAM - PubMed Abstract:
Secretory pathway Ca 2+ /Mn 2+ ATPase 1 (SPCA1) actively transports cytosolic Ca 2+ and Mn 2+ into the Golgi lumen, playing a crucial role in cellular calcium and manganese homeostasis. Detrimental mutations of the ATP2C1 gene encoding SPCA1 cause Hailey-Hailey disease. Here, using nanobody/megabody technologies, we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of human SPCA1a in the ATP and Ca 2+ /Mn 2+ -bound (E1-ATP) state and the metal-free phosphorylated (E2P) state at 3.1- to 3.3-Å resolutions. The structures revealed that Ca 2+ and Mn 2+ share the same metal ion-binding pocket with similar but notably different coordination geometries in the transmembrane domain, corresponding to the second Ca 2+ -binding site in sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ -ATPase (SERCA). In the E1-ATP to E2P transition, SPCA1a undergoes similar domain rearrangements to those of SERCA. Meanwhile, SPCA1a shows larger conformational and positional flexibility of the second and sixth transmembrane helices, possibly explaining its wider metal ion specificity. These structural findings illuminate the unique mechanisms of SPCA1a-mediated Ca 2+ /Mn 2+ transport.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi 980-8577, Japan.