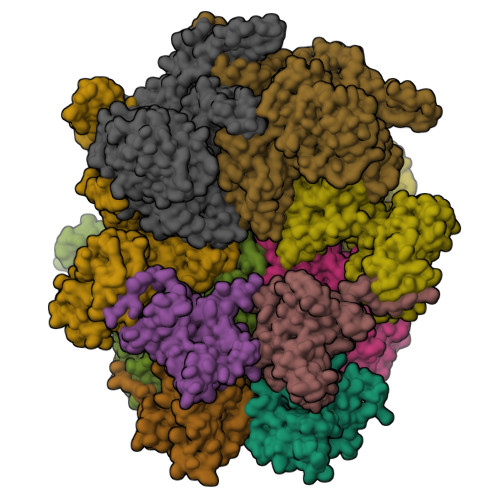
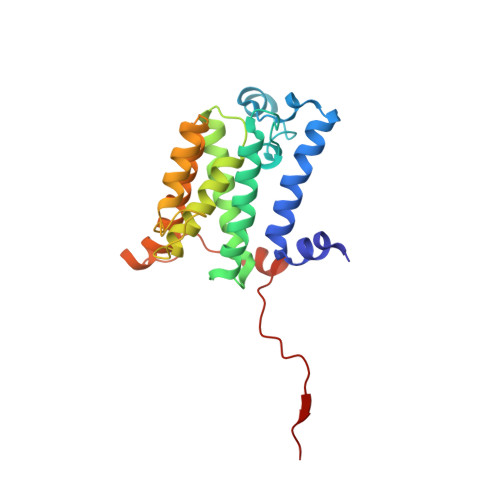
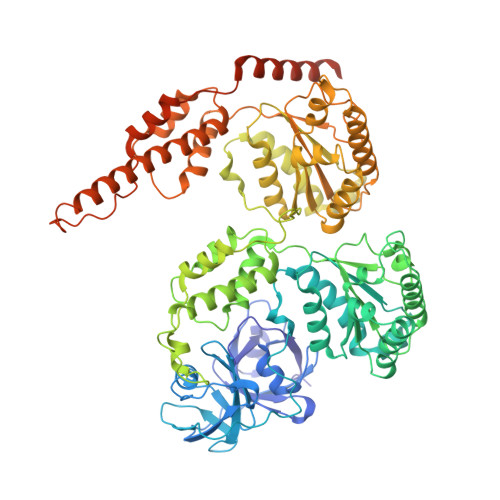
The cryo-EM structure of the human ERAD retrotranslocation complex.
Rao, B., Wang, Q., Yao, D., Xia, Y., Li, W., Xie, Y., Li, S., Cao, M., Shen, Y., Qin, A., Zhao, J., Cao, Y.(2023) Sci Adv 9: eadi5656-eadi5656
- PubMed: 37831771
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi5656
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Y4W, 7Y53, 7Y59 - PubMed Abstract:
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) maintains protein homeostasis by retrieving misfolded proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen into the cytosol for degradation. The retrotranslocation of misfolded proteins across the ER membrane is an energy-consuming process, with the detailed transportation mechanism still needing clarification. We determined the cryo-EM structures of the hetero-decameric complex formed by the Derlin-1 tetramer and the p97 hexamer. It showed an intriguing asymmetric complex and a putative coordinated squeezing movement in Derlin-1 and p97 parts. With the conformational changes of p97 induced by its ATP hydrolysis activities, the Derlin-1 channel could be torn into a "U" shape with a large opening to the lipidic environment, thereby forming an entry for the substrates in the ER membrane. The EM analysis showed that p97 formed a functional protein complex with Derlin-1, revealing the coupling mechanism between the ERAD retrotranslocation and the ATP hydrolysis activities.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Orthopaedics, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Implant, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.