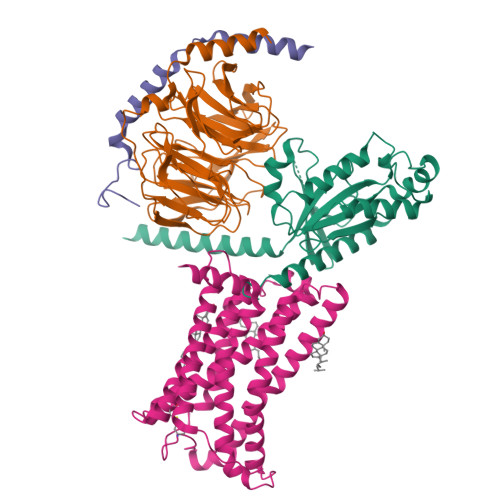
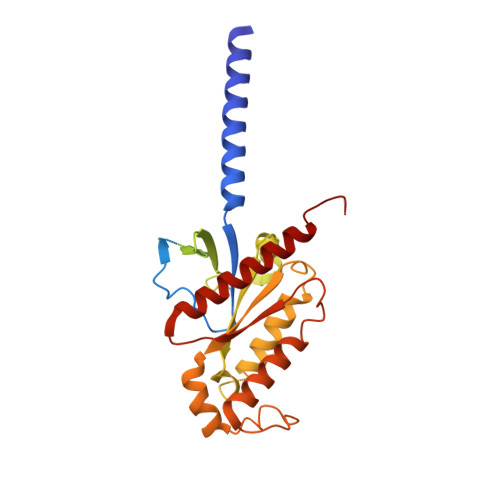
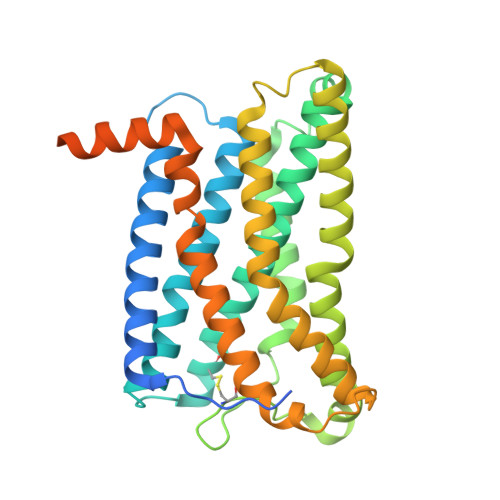
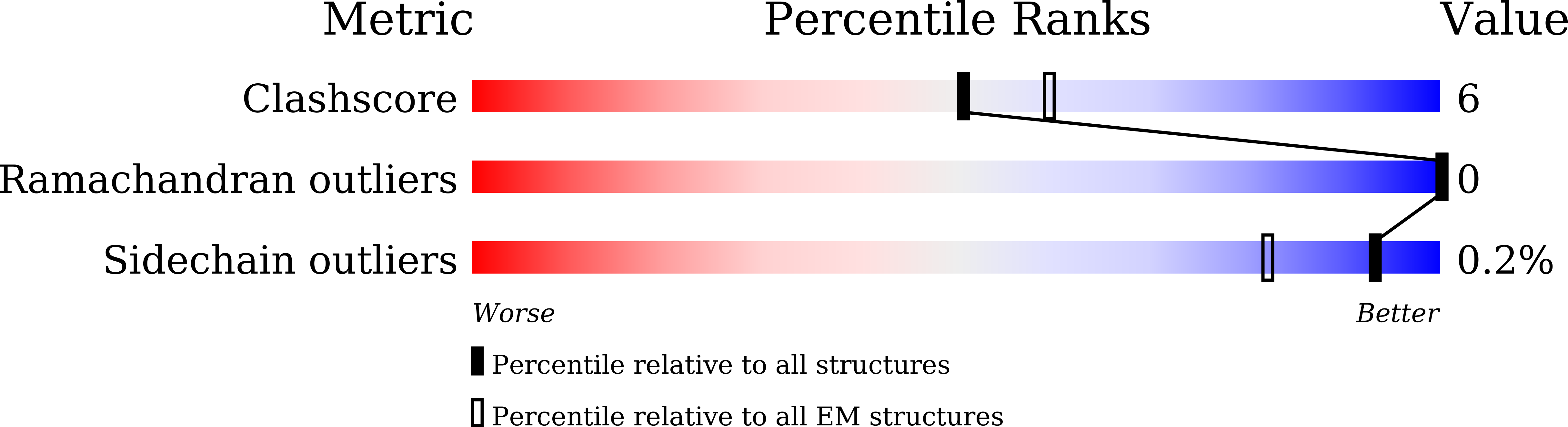Activation of the human chemokine receptor CX3CR1 regulated by cholesterol.
Lu, M., Zhao, W., Han, S., Lin, X., Xu, T., Tan, Q., Wang, M., Yi, C., Chu, X., Yang, W., Zhu, Y., Wu, B., Zhao, Q.(2022) Sci Adv 8: eabn8048-eabn8048
- PubMed: 35767622
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abn8048
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XBW, 7XBX - PubMed Abstract:
As the only member of the CX3C chemokine receptor subfamily, CX3CR1 binds to its sole endogenous ligand CX3CL1, which shows notable potential as a therapeutic target in atherosclerosis, cancer, and neuropathy. However, the drug development of CX3CR1 is hampered partially by the lack of structural information. Here, we present two cryo-electron microscopy structures of CX3CR1-G i1 complexes in ligand-free and CX3CL1-bound states at 2.8- and 3.4-Å resolution, respectively. Together with functional data, the structures reveal the key factors that govern the recognition of CX3CL1 by both CX3CR1 and US28. A much smaller conformational change of helix VI upon activation than previously solved class A GPCR-G i complex structures is observed in CX3CR1, which may correlate with three cholesterol molecules that play essential roles in conformation stabilization and signaling transduction. Thus, our data deepen the understanding of cholesterol modulation in GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor) signaling and provide insights into the diversity of G protein coupling.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zuchongzhi Road, Pudong, Shanghai 201203, China.