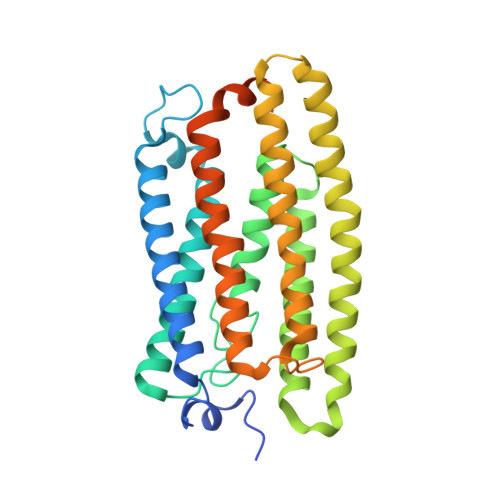
Structural basis for channel conduction in the pump-like channelrhodopsin ChRmine.
Kishi, K.E., Kim, Y.S., Fukuda, M., Inoue, M., Kusakizako, T., Wang, P.Y., Ramakrishnan, C., Byrne, E.F.X., Thadhani, E., Paggi, J.M., Matsui, T.E., Yamashita, K., Nagata, T., Konno, M., Quirin, S., Lo, M., Benster, T., Uemura, T., Liu, K., Shibata, M., Nomura, N., Iwata, S., Nureki, O., Dror, R.O., Inoue, K., Deisseroth, K., Kato, H.E.(2022) Cell 185: 672
- PubMed: 35114111
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7W9W - PubMed Abstract:
ChRmine, a recently discovered pump-like cation-conducting channelrhodopsin, exhibits puzzling properties (large photocurrents, red-shifted spectrum, and extreme light sensitivity) that have created new opportunities in optogenetics. ChRmine and its homologs function as ion channels but, by primary sequence, more closely resemble ion pump rhodopsins; mechanisms for passive channel conduction in this family have remained mysterious. Here, we present the 2.0 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of ChRmine, revealing architectural features atypical for channelrhodopsins: trimeric assembly, a short transmembrane-helix 3, a twisting extracellular-loop 1, large vestibules within the monomer, and an opening at the trimer interface. We applied this structure to design three proteins (rsChRmine and hsChRmine, conferring further red-shifted and high-speed properties, respectively, and frChRmine, combining faster and more red-shifted performance) suitable for fundamental neuroscience opportunities. These results illuminate the conduction and gating of pump-like channelrhodopsins and point the way toward further structure-guided creation of channelrhodopsins for applications across biology.
Organizational Affiliation:
Komaba Institute for Science, The University of Tokyo, Meguro, Tokyo, Japan.