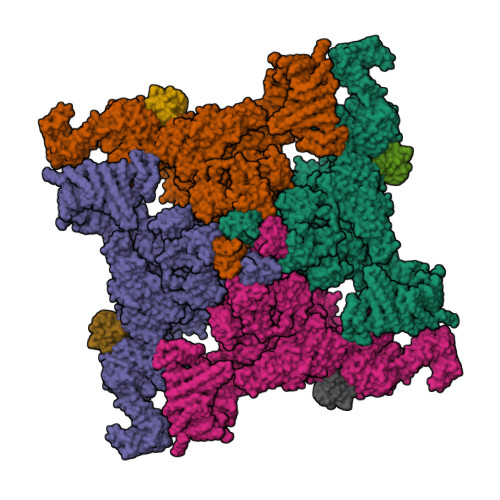
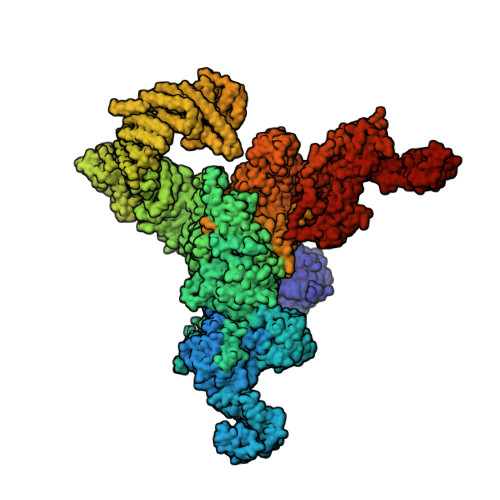
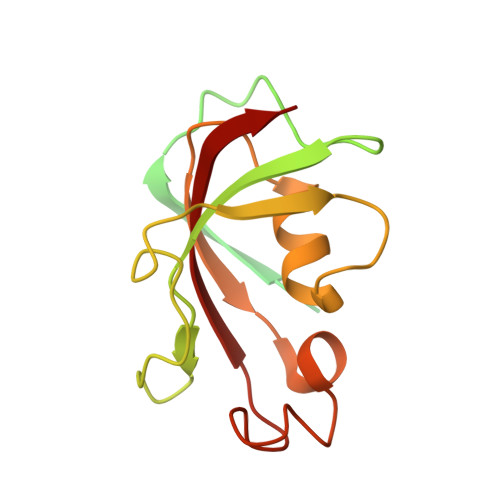
Molecular basis for gating of cardiac ryanodine receptor explains the mechanisms for gain- and loss-of function mutations.
Kobayashi, T., Tsutsumi, A., Kurebayashi, N., Saito, K., Kodama, M., Sakurai, T., Kikkawa, M., Murayama, T., Ogawa, H.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 2821-2821
- PubMed: 35595836
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30429-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VML, 7VMM, 7VMN, 7VMO, 7VMP, 7VMR - PubMed Abstract:
Cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) is a large Ca 2+ release channel in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and indispensable for excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. RyR2 is activated by Ca 2+ and RyR2 mutations are implicated in severe arrhythmogenic diseases. Yet, the structural basis underlying channel opening and how mutations affect the channel remains unknown. Here, we address the gating mechanism of RyR2 by combining high-resolution structures determined by cryo-electron microscopy with quantitative functional analysis of channels carrying various mutations in specific residues. We demonstrated two fundamental mechanisms for channel gating: interactions close to the channel pore stabilize the channel to prevent hyperactivity and a series of interactions in the surrounding regions is necessary for channel opening upon Ca 2+ binding. Mutations at the residues involved in the former and the latter mechanisms cause gain-of-function and loss-of-function, respectively. Our results reveal gating mechanisms of the RyR2 channel and alterations by pathogenic mutations at the atomic level.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.